The 16 Most Helpful Languages for Travelers to Learn
Travel and language were made for each other.
If you need reasons to learn a foreign language, travel is definitely a good one.
In fact, travelers have more reason than just about anyone else to learn a new language!
If you dream of going to far-off lands and speaking with the locals like it’s nothing, then this post is for you.
Keep reading for the best languages to learn for travel, why you should learn one and how to do it.
Contents
- 1. English
- 2. Spanish
- 3. Mandarin Chinese
- 4. French
- 5. Arabic
- 6. German
- 7. Russian
- 8. Portuguese
- 9. Cantonese
- 10. Thai
- 11. Indo-Malay
- 12. Hindustani
- 13. Bengali
- 14. Farsi
- 15. Swahili
- 16. Shona
- Other World Languages to Learn for Travel
- Why Travelers Should Study Languages
- How to Learn a Language for Travel
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
1. English
Most useful in: Every continent, but North America and Europe in particular
As you’re probably well aware, English is the modern world’s lingua franca.
Throughout the last century, English has grown in international importance. Though it stemmed from Britain’s colonial conquests, it also owes much of its global prominence to American imperialism.
English is less varied throughout North America, and most speakers should understand just about everything they hear from the most remote parts of Canada to either coast of the U.S., though English could also be called “the European traveler’s best friend.”
Thanks to high levels of education and a decidedly global outlook, English is particularly handy in Europe. You shouldn’t expect to get into deep philosophical debates in Italian coffee shops or Russian bars, but you can count on finding enough English speakers to at least give you basic assistance and a little company in nearly every large city throughout the continent.
In fact, throughout most parts of the world frequented by tourists, people understand at least a few basic English travel phrases.
2. Spanish
Most useful in: South and Central America, Europe
Spanish is another handy world language for travelers in Europe. Outside Spain, its commonalities with Portuguese and Italian will help you get through its southern European neighbors as well.
Where Spanish really shines, however, is in Latin America—it’s the unifying force from the Rio Grande to Patagonia and beyond. Additionally, most Spanish-speaking travelers will find Texas, Arizona, New Mexico, California and South Florida all relatively easy to navigate in Spanish; most large North American cities have sizable Hispanic populations, as well.
Don’t get discouraged if you learn the language and can’t understand it in some regions. Parts of the Caribbean and the Southern Cone of South America are notoriously difficult for non-natives and even some native Spanish speakers to understand.
One should also be forewarned that remote areas of the Americas, especially in southern Mexico and Andean countries, may lack Spanish speakers entirely and instead have large populations who speak an indigenous language as their first (and possibly only) language.
Some pre-trip classes or just a few important Spanish phrases will be majorly helpful in these parts of the world.
3. Mandarin Chinese
Most useful in: East Asia
As not only the language with the most speakers in the world but also the official state language of the largest country in Asia, Mandarin Chinese is an obvious big name on this list.
Many visitors to China arrange to take organized tours, often led by Mandarin-speaking officials. While English tours are certainly available, speaking a bit of Chinese will almost certainly ingratiate you to your guide and any locals you get a chance to meet.
For the even more adventurous, a sturdy level of Mandarin will help you navigate the enormous country of China more independently, although you’ll find there are a vast amount of dialects with varying degrees of mutual intelligibility.
Mandarin is also the official language of Taiwan, a radical travel alternative to Mainland China. Although the island nation doesn’t technically exist according to most of the world, knowing some Chinese will help you better enjoy its tropical weather, high level of development and relatively cheap cost of travel and living.
4. French
Most useful in: Europe, the Middle East, the Americas, North Africa
French isn’t only a good choice for France, but it’s also still popularly learned by educated people throughout Europe.
Further, large parts of North Africa and the Middle East were parts of the French Empire before World War II, and the French language remains prominent and even official in many of the former colonies. The vast majority of middle-class people in Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Lebanon still speak fluent French.
French will also serve well in Quebec, French Guiana and the Caribbean Islands, and might open up some interesting chats in southern Louisiana, where Cajun French still runs strong. Throughout mainland Southeast Asia as well, older, educated citizens of the former French colonies of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos are likely to speak some of the colonial language.
There’s a high likelihood that many people you meet in cities will be fluent in French, and you may find that many are happy to chat with a curious traveler, if you have the must-know French travel phrases under your belt.
5. Arabic
Most useful in: The Middle East, Northern Africa
Modern Standard Arabic is a good starting point for anyone interested in this multifaceted language, but you can choose a specific variety of Arabic if you have a certain destination in mind.
Egyptian Arabic is a common choice. This isn’t just because of its relative economic and political power, or the fact that Egypt is the most populous Arab country, but because the Hollywood of the Arab World is in Cairo, the heart of both Arab cinema and the place where most foreign films are dubbed.
Another option is Gulf Arabic, one of the widest-reaching dialects. This version is used and understood throughout the Gulf States and in large swaths of Saudi Arabia.
In general, Arabic is an increasingly popular choice for language learners because of its up-and-coming economic potential.
6. German
Most useful in: Europe
German is your all-access pass to central Europe and beyond.
Germany is close to the geographic, political and financial centers of Europe, so it makes sense that this powerful country’s equally powerful language penetrates far and wide. Native-speaking countries include Switzerland, parts of Belgium and Luxembourg, Austria and mother Germany herself.
The German language will come in handy far beyond these borders, however. Young people throughout the Netherlands, the UK and Central Europe are learning German more and more as its namesake country increasingly offers jobs and opportunities to young Europeans.
The youths aren’t the only ones who know a bit of Deutsch, though. Huge guest worker populations from Eastern Europe and the Balkans have now spent several decades working in Austria and Germany, leaving many members of the middle generation of these countries fairly proficient German speakers.
A few common phrases will be sure to make your Central European tour sehr gut (very good).
7. Russian
Most useful in: Europe, Asia
The official language of Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan will see you from the Baltic Sea all the way to the Bering Strait.
While the Soviet Union never existed in many young travelers’ lifetimes, one of its convenient legacies is the widespread use of the Russian language it left behind.
Aside from the countries in which it’s an official state language, there’s a long list of other Eastern European and West Asian countries that formally recognize Russian as a minority language, including Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Moldova, Georgia, Romania and Norway.
And, while not official, its important role as a significant minority language or inter-ethnic language will assure Russian-speaking travelers easy communication in part or most of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania, Mongolia and Uzbekistan, as well.
8. Portuguese
Most useful in: Africa, South America, Europe
Portuguese is of course the language of Portugal, though Brazilian Portuguese is just as (if not more) popular than its European counterpart.
It could be just the language you want to learn for travel through South America, in fact. While it’s limited to one country of the continent, Brazil happens to be the fifth-largest country in the world, full of some of the most appealing tourist destinations in the world.
But Portuguese, as a result of many years of colonialism, is also spoken in a geographically scattered collection of African countries: Mozambique, Angola, Guinea-Bissau and the island nation of São Tome and Principe.
Angola is notoriously stingy with its tourist visas, making it nearly impossible for Western travelers to get in, and thus making it something of an internationally undiscovered gem. Mozambique and Guinea-Bissau aren’t as difficult to travel to, but you’ll find their infrastructure reflects the fact that all three are among the least developed countries in the world.
9. Cantonese
Most useful in: Southern China
Sometimes forgotten in the shadow of big brother Mandarin, Cantonese is another enormous world language spoken both in China and beyond its borders.
As the most prestigious variety of the Yue language, Cantonese (along with other languages with which it’s mutually intelligible) is used by 60 million speakers spread across southern China, Hong Kong and Macau.
Cantonese has a bit more geographic reach than Mandarin, as the vast majority of Chinese expat communities in East and Southeast Asia—and in most of the world—are Cantonese speakers. From the Yokohama Chinatown on Tokyo’s south side to the capitals of Southeast Asia, in almost any big Asian city, you’ll find at least a small community of Cantonese speakers.
10. Thai
Most useful in: Southeast Asia
This is a language that’s practically begging travelers to become expats.
Thailand is currently one of the most popular destinations for “digital nomads,” people who work remotely from their laptops (particularly Westerners, it seems).
If you’re looking to go location independent or just want to spend a few months in one of the cheapest expat-friendly countries in the world, then some Thai lessons would help you get a deeper and more authentic experience of the country.
Beyond Thailand’s borders, some Thai speakers will also understand Laotian, spoken in its even cheaper but less developed neighboring country, making a Laotian vacation an excellent option for Thai-speaking expats based in popular cities like Chiang Mai or Bangkok.
11. Indo-Malay
Most useful in: Southeast Asia, Oceania
The fuzzy boundary between the Indonesian and Malaysian languages coincides with the fuzzy geographic boundary between what’s conventionally known as Southeast Asia and Oceania.
Largely because of those fuzzy boundaries, learning the language referred to in Malaysia as “Malay” and in Indonesia as “Indonesian” will put you in touch with about a quarter of a billion locals scattered across these thousands of islands.
Also helpful is the fact that it’s incredibly easy to learn: Indo-Malay’s lack of verb tenses and simple grammar means a couple weeks of intensive courses at the beginning of your trip should leave you reasonably prepared for everyday basic communication—and if you stick to it, your skills will only improve as you hop from island to island.
12. Hindustani
Most useful in: Asia
Hindustani is the super-language of India and Pakistan. India is already a hot backpacking and luxury travel destination, and Pakistan is steadily climbing its way up as it improves its security and infrastructure.
Between these two giant countries, four hundred million native and second language speakers use Hindi or Urdu, two standard dialects of the giant language linguists call Hindustani.
Throughout northern India and most of Pakistan, Hindi or Urdu will be spoken by nearly everyone you meet, and for many people this will be their native language (the English they learned in school takes a back seat as a third or fourth language for most).
A few well-placed phrases in Hindi or Urdu are your best shot at charming your way into the hospitality and natural beauty of India and Pakistan.
13. Bengali
Most useful in: Asia
Sandwiched between giants like India and China, plus the tourist attractions of Southeast Asia, Bengali is still a great language for travelers, especially those looking to be on the cutting edge.
There are 200 million speakers in Bangladesh and India’s Bengal province. Bangladesh and the neighboring Indian province are densely populated parts of the Bay of Bengal, with some of the most beautiful and undiscovered wildlife in the world.
Bangladesh hasn’t really reached mainstream travel itineraries yet, but its tourism industry is growing. If you want to get there before it gets cool, brush up on your Bengali and book a flight!
14. Farsi
Most useful in: The Middle East
This is the official language of Iran. Americans may still have more trouble getting visas than others, but this country is a rapidly up-and-coming travel destination.
Ask any backpacker who’s been there and they’ll rave about hospitality, openness and well-educated people. Imagine how much more of that you could soak up with some basic Farsi!
The same language, under various different national names, is spoken in Afghanistan and parts of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. While that first name probably won’t be a popular vacation destination any time soon, the latter two are becoming more and more common legs of Central Asian tours.
15. Swahili
Most useful in: East Africa
Swahili is East Africa’s own lingua franca. While native to only a small population of five million or so, it’s spoken and understood by 150 million people, stretching from eastern parts of the Congo to the Indian Ocean shores of Tanzania and Kenya.
The majority of the most spectacular safari countries are situated in the Swahili language area, so speaking the language might allow you to take a more authentic safari or another tour that’s more geared towards locals.
16. Shona
Most useful in: Southeast Africa
Though among the poorest regions on earth, Southeast Africa is also raved about by visitors as one of the friendliest and most welcoming.
From the hippo-filled Okavango Delta of Botswana, throughout Zimbabwe and to the remote northern beaches of Mozambique, Shona is the mother tongue of most locals you’ll meet.
Learn a few words of Shona and visit the nature of the Zimbabwean countryside, or enjoy the well-maintained roads and highly developed cities of Botswana. Even simple phrases like “thank you” or “your country is beautiful” are sure to endear you to everyone you meet.
Other World Languages to Learn for Travel
Depending on where you plan on going, you may want to make your language learning even more niche than some of the options above.
Here are a few additional languages you might choose to learn to make your global travels a bit smoother, or at least a bit friendlier:
- Japanese is spoken by a large population, with 125 million speakers, but its limitation to travelers is that it doesn’t go very far outside Japan.
- Korean is spoken by about 75 million people, although a good number of them are in North Korea (still not very tourist friendly) and the rest are mostly in South Korea, so it’s also a relatively location-specific tongue as well.
- Dutch is the national language of Suriname and six Caribbean Islands, and it’s an official language in Belgium and the Netherlands in Europe, too.
- Quechua is one of the biggest indigenous languages of the Andes, and will get you far in more remote areas of South America.
- The Serbo-Croatian dialects of the Balkans are all mutually intelligible, and will give you a priceless opportunity to ditch the resorts and explore natural beauty that can’t be beat in the rest of Europe.
- Turkish will help you not only in Turkey but also in regions that speak similar Turkic languages in Central Asia.
- Hausa in West Africa is a large Bantu language with many millions of speakers and lots of mutually intelligible dialects.
- Amharic is spoken by nearly 22 million people in Ethiopia, which is arguably the African continent’s most culturally distinct country due to its unique history.
- Telugu can be handy in South Asia, specifically in India, as it’s spoken and understood throughout several of the southern states.
- Tibetan will give you priceless access to cultural opportunities if you want to trek into the remote regions of Tibet and northern China in Asia.
- Tagalog is the official language of the Philippines in Southeast Asia, and Spanish speakers will find it easy and even familiar.
Of course, there are plenty of factors to consider when deciding which language to learn. Perhaps the most important aspect, however, is your interest in said language.
If you’re planning to travel to a place that speaks a foreign tongue, that likely means you’re interested in the culture and the way of life in that place. This is great motivation for when language learning seems a bit more challenging than you expected.
So, if you really don’t know what language to learn for your travels, pick the one that captures your attention the most!
Why Travelers Should Study Languages
Language learning takes time and effort. If you’re on the fence about whether it’s really worth learning a language for your travels, let me argue in favor of it with these points:
- The local language can help you during your travels. You may be able to haggle and get discounts. You can ask for directions and assistance. It might even save your life (or at least some money) in case of emergencies.
- You’ll have a more authentic travel experience. Language is the key to a treasure chest full of history, authentic cultural experiences and new friends. You’ll be able to find out what a place is really like by chatting with locals, who can usually offer advice, tips and/or company on your excursions.
- The right language(s) can take you many places. You may have noticed that many languages on the list above are spoken in more than one country, and often (thanks to colonialism) on more than one continent, too. By knowing more than one or two languages, you greatly increase your ability to communicate anywhere in the world.
- You’ll be a more respectful traveler. Anyone planning on spending more than a few days in a foreign region should devote some time to learning at least a dozen or so polite phrases in the local language.
Despite the fact that many people around the world speak English, most will be quite insulted if they feel visitors expect them to speak and understand it. Even just learning simple travel phrases like “I’m sorry, I don’t speak your language, do you speak English?” will distance you from off-putting images of rude, entitled tourists.
How to Learn a Language for Travel
There are many resources and blogs out there for learning a language that will help you prepare for your journey.
To get ready for a trip abroad, you can start by reading travel guides and phrasebooks—you’ll arrive knowing about the destinations, local language, culture, etiquette and customs. Lonely Planet has travel guides and phrasebooks for virtually every region and language under the sun, so it’s a great place to start learning.
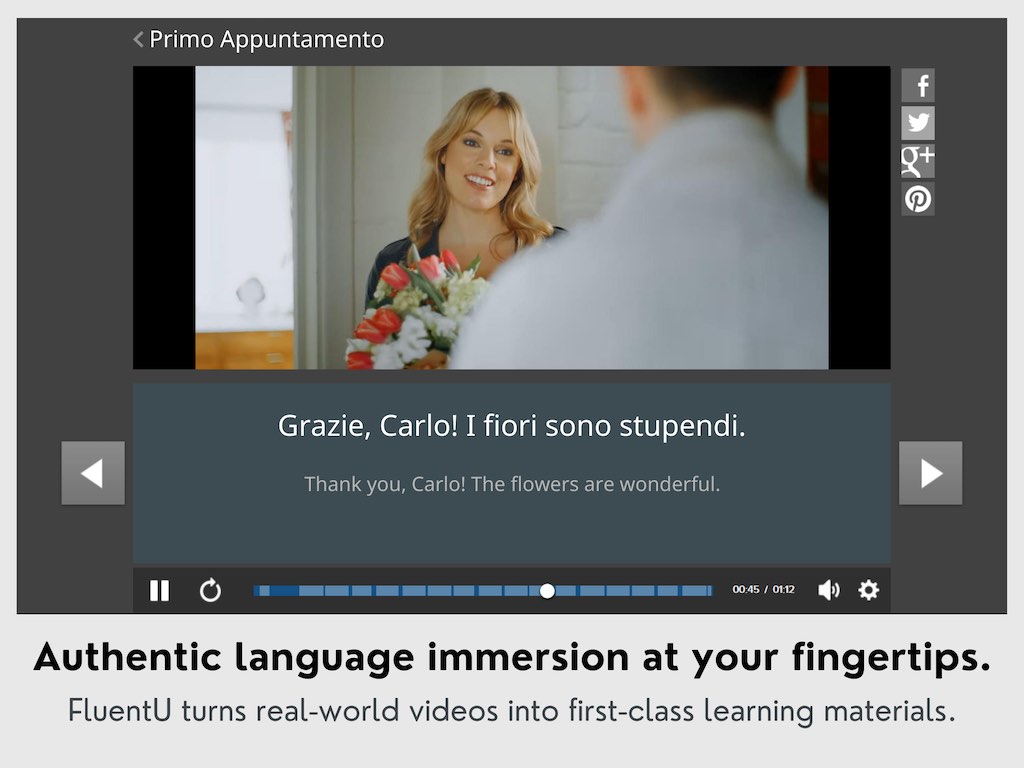
Apps are also an option if you prefer pocket-sized language guides. Dictionaries and flashcard apps are super handy for immediate translations and language practice, while programs like FluentU are helpful for authentic language immersion whenever you have time to spare.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Anything you can do to prepare yourself before traveling makes a difference. But if you want to continue learning while you’re on the go, you have additional options:
- Teach English in your destination country. If you’re reading this, chances are you speak English. Use this skill by teaching as you travel. The best part is that you generally don’t need previous experience to start. Teaching English will also offer you a way to earn money as you travel.
- Live with a host family. This is a great way to learn a language. Living with people who speak your target language means you’ll hear and use it every day out of sheer necessity. In fact, immersion language learning is one of the most effective and natural ways to learn a new language.
- Volunteer. Volunteering with a local non-profit or humanitarian organization is also a great way to learn new languages while traveling—with the bonus that you’ll be helping people in need at the same time.
- Ask lots of questions. Actually using the language is perhaps the fastest way to learn it. Ask locals about their favorite restaurants or places to visit, or ask for directions (even if you already know where you’re going!). Remember: When it comes to learning a language, the focus isn’t the destination but the people you’ll learn from along the way!
We know there are a ton of benefits for learning a language, but no one benefits from it as much as a world traveler.
If you’re planning a big trip in the near future or dreaming of traveling the world one day, you can start brushing up on your language skills today!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you dig the idea of learning on your own time from the comfort of your smart device with real-life authentic language content, you'll love using FluentU.
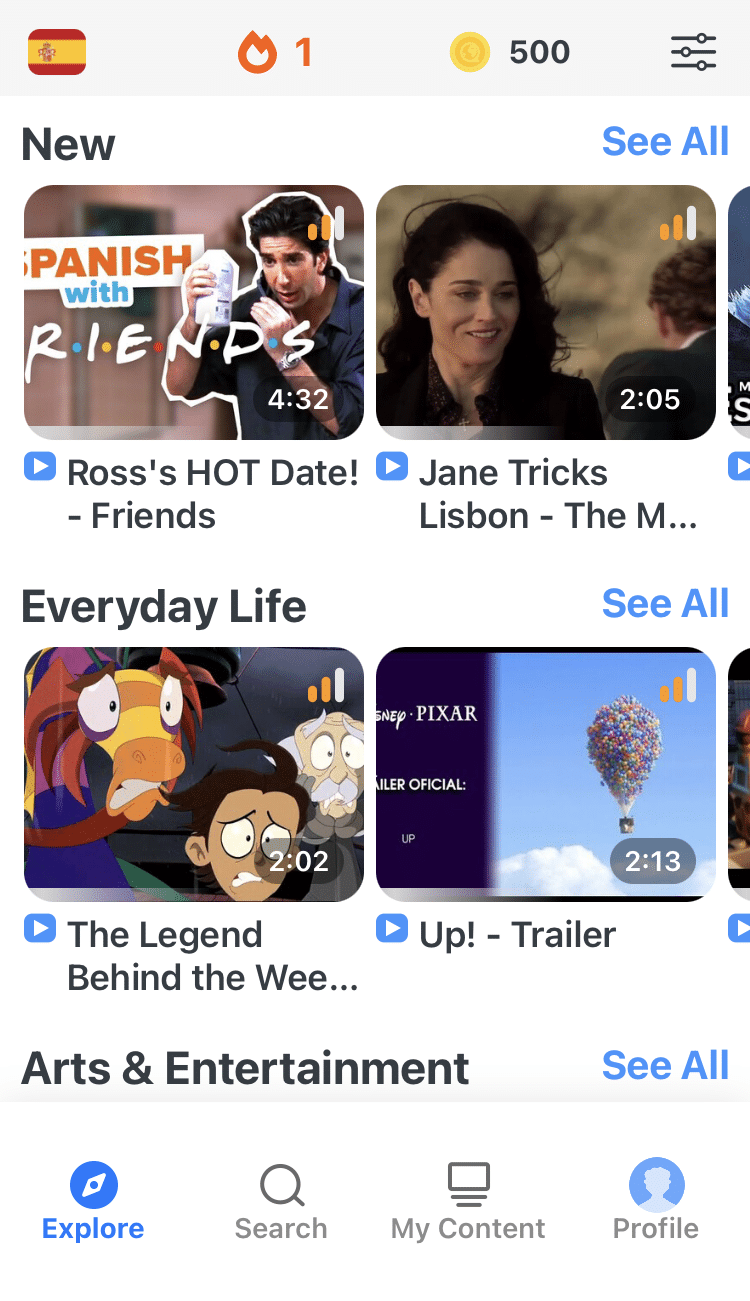
With FluentU, you'll learn real languages—as they're spoken by native speakers. FluentU has a wide variety of videos as you can see here:
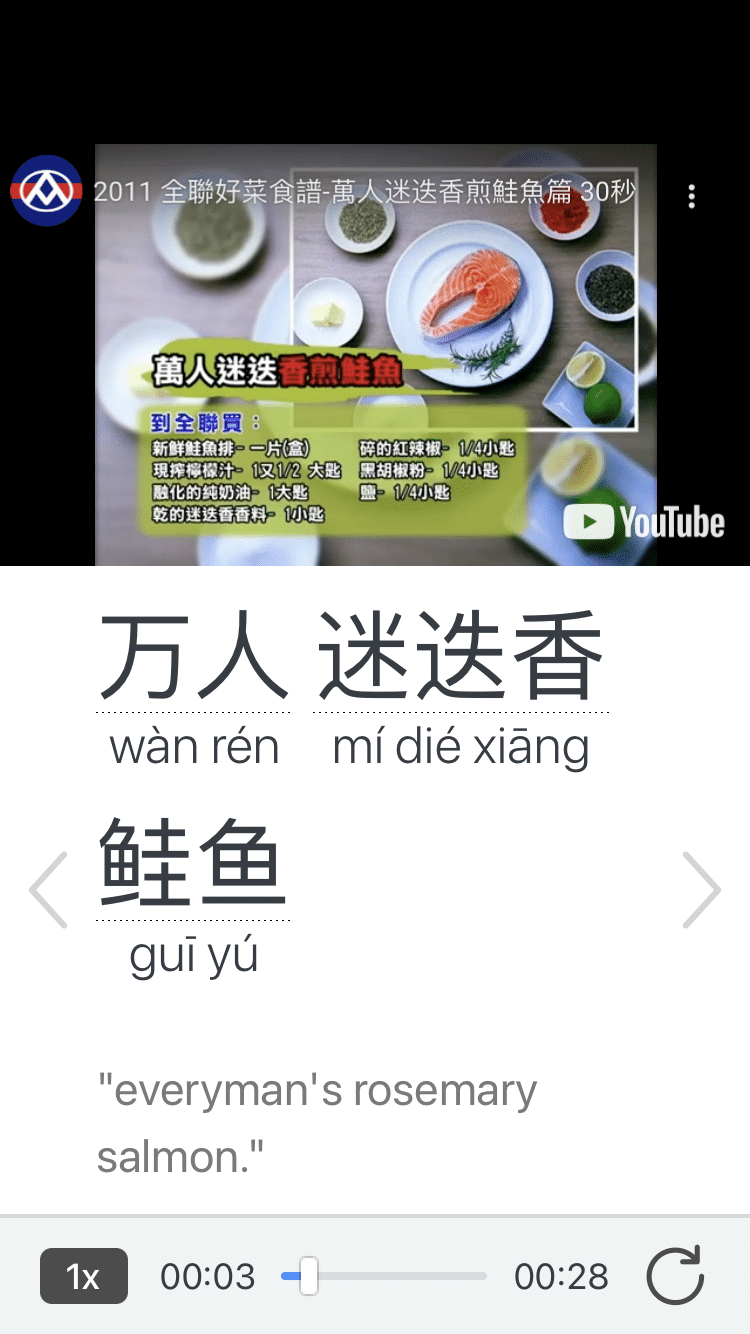
FluentU has interactive captions that let you tap on any word to see an image, definition, audio and useful examples. Now native language content is within reach with interactive transcripts.
Didn't catch something? Go back and listen again. Missed a word? Hover your mouse over the subtitles to instantly view definitions.
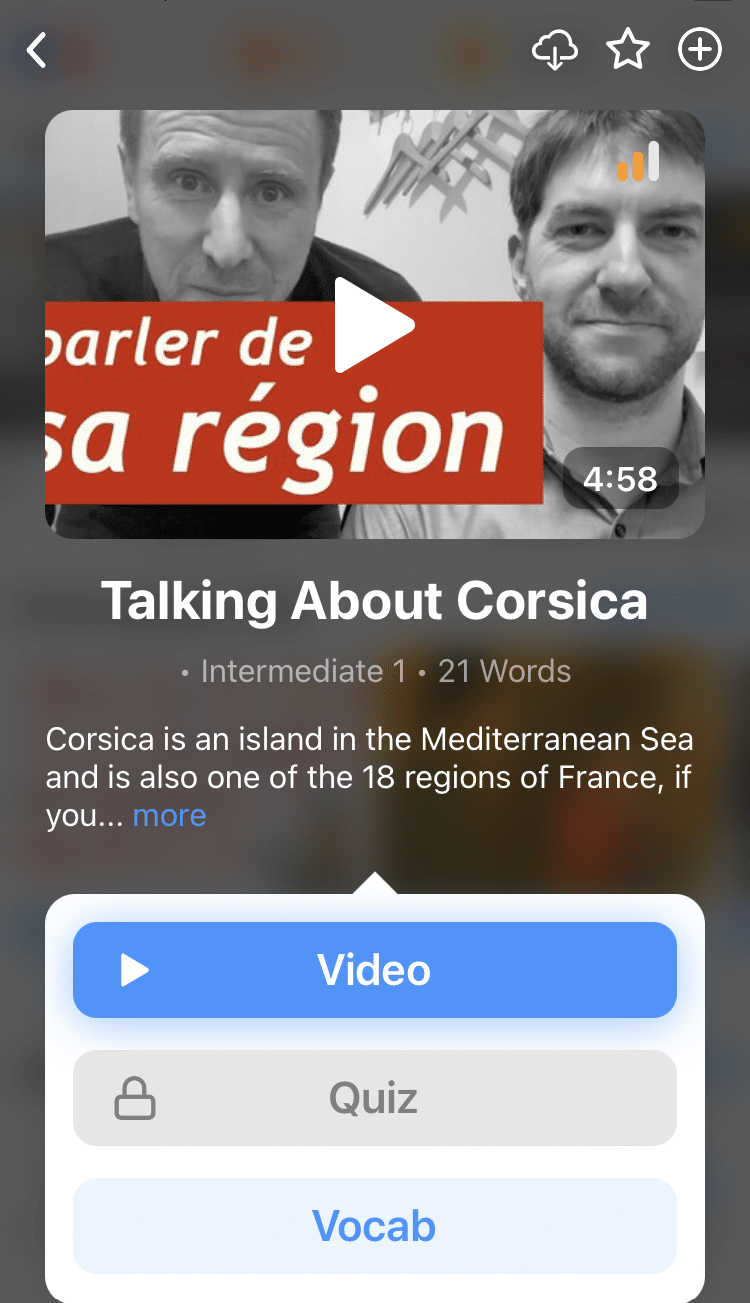
You can learn all the vocabulary in any video with FluentU's "learn mode." Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
And FluentU always keeps track of vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You get a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)