Past Tense vs. Past Participle
Many English learners are confused about the difference between the past tense and past participle verb forms.
It’s easy to see why. After all, the two forms of the verb are often identical.
But have no fear. I’m here to help you out.
By the time you finish with this post, you should understand that there are clear differences between the past tense and the past participle verb form, even if they often look alike.
Contents
- The Difference Between Past Tense and Past Participle
- Forming the Past Participle
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
The Difference Between Past Tense and Past Participle
Basically, the past tense is a true verb tense while the past participle is a verb-derived form that has three distinct uses.
Since past participle verbs are not tenses, they can’t be used on their own. You need an auxiliary verb such as “have” or “had.” Because of this, the past participle is commonly used as a compound verb.
The past tense, on the other hand, is a conjugated verb that expresses that an action has happened in the past, or has previously existed (but no longer).
What Is the Past Tense?
The past tense is one of three tenses in English:
- Past tense
- Present tense
- Future tense
This concept of tenses is reflected in the way we conjugate verbs.
These tenses can further be divided into four distinct forms (simple, continuous, perfect and perfect continuous). For the past tense, they are:
- Simple past (I went to Paris.)
- Past continuous (I was studying when the phone rang.)
- Past perfect (I had eaten lunch by 11:00.)
- Past perfect continuous (I had been eating since I woke up last Tuesday.)
Simple Past Tense
You use this tense when the action has already happened or has been completed.
- I ate a chicken sandwich.
- I went on a cruise last summer.
Past Continuous Tense
We use this to refer to something in the past that has already happened, but as though it were still happening (usually in the context of another event).
- I was eating a chicken sandwich when he called me.
- Sara was sunbathing when the rainstorm started.
The “-ing” verb gives us the impression of an action that is happening, while the “was” means that it took place in the past.
Past Perfect Tense
We usually use this to talk about events that have already been completed before a specified time or another event.
- I had eaten a chicken sandwich that my mother had made for me.
- The package had been delivered before I got home.
The use of the verb “had” along with the specific verb form “eaten” (which is the participle form) tells us that it’s in the past perfect.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Finally, we use this verb form to refer to an action that was still happening until another event occurred.
- I had been eating chicken sandwiches from the local diner until I learned to cook on my own.
- She had been studying for hours before she finally understood the concept.
What Is the Past Participle?
The past participle—one of two participles in English—is a verb-based word form that has three uses:
- to form the perfect tenses
- as an adjective
- to form the passive voice
Past Participle and Past Perfect Verb Tense
To form a past perfect verb phrase, you need an auxiliary verb (had) and a past participle word, like in these examples:
- She had already eaten dinner when I arrived at her house.
- The train had departed by the time we reached the station.
- They had finished the project before the deadline.
- By the time he woke up, his friends had already left.
- The movie had already started when we got to the theater.
As you can see in a couple of these examples, the “had” and the past participle can sometimes have an adverb between them, such as “already.”
Past Participle and Passive Voice
Past participles can also be used to form the passive voice. This form is often used in academic writing, or to de-emphasize the agent/subject of a sentence, or the person or thing performing the main action.
To form the passive voice, the past participle is used in combination with either “was” or “were.”
- The car was driven by Max.
- The houses were built in the 19th century.
- The painting was admired by many visitors at the art exhibition.
- The project was completed ahead of schedule.
You can refresh your memory on the differences between active and passive voice here.
Past Participle as an Adjective
Past participles can also be used as adjectives. To do this, they are in the exact same form as they are in the past perfect tense.
- The broken vase lay shattered on the floor.
- The excited children ran to the playground.
- The stolen jewels were recovered by the police.
- She was wearing a beautiful embroidered dress.
- The exhausted hiker collapsed onto the ground.
Forming the Past Participle
Forming the past participle is pretty easy, except for the fact that there are quite a few irregular ones.
Regular Past Participles
For most verbs, the simple past and the past participle forms of the verb are the same, so you probably already know how to form them.
Just add the suffix “-ed” (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”).
Irregular Past Participles
However, some other past participles are formed differently, and some don’t look like their past tense forms.
Irregular participles don’t follow a specific pattern and can have many different endings such as: “-en,” “-n,” “-ne” and “-t.”
The best way to learn the irregular past participles is by memorizing them. Here are a few more irregular verbs in their past and past participle forms.
| Infinitive | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Awake | Awoke | Awoken |
| Drive | Drove | Driven |
| Fly | Flew | Flown |
| See | Saw | Seen |
| Take | Took | Taken |
| Forget | Forgot | Forgotten |
| Grow | Grew | Grown |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen |
| Sink | Sank | Sunk |
OK, that’s it. You now know the differences between the past tense and the past participle and can form them on your own, right?
To practice, look up a news article online and try to find some words you think are past tense or part participles. Then take a guess which type of word they are.
You can also find examples in use in English videos. Listen closely for how and when the two are formed.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Practice makes perfect, or rather: “Through diligent practice, the student had mastered the past participle, proving once again that practice makes perfect.”
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
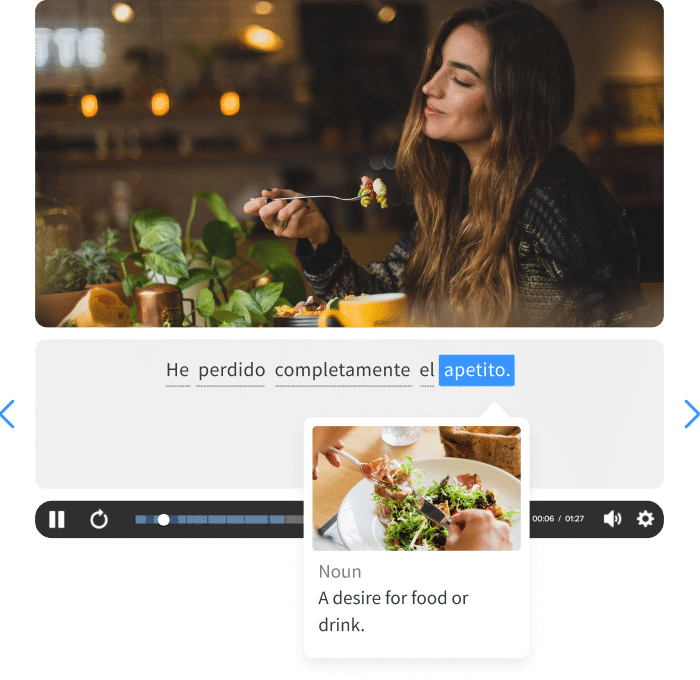
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
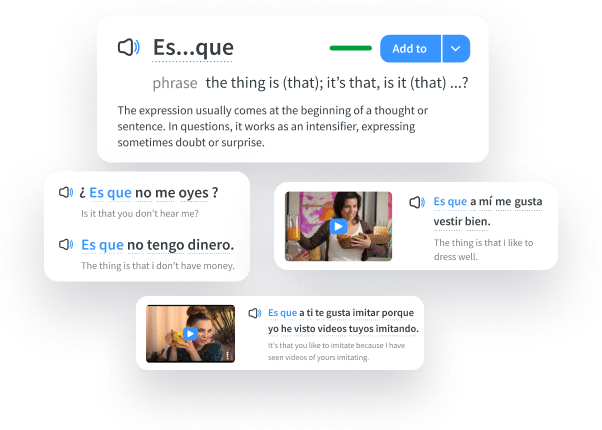
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)