Has vs. Have
As an English learner, you probably see the English words “has” and “have” frequently.
If you’re a beginner English speaker, you might be confused about how to use them. In that case, you’ve come to the right post.
We’re going to crack the code and solve the mystery of “has” vs. “have.”
Read on to find out about their main differences and how to use each properly, plus handy practice resources!
Contents
- “Has” vs. “Have”: What’s the Difference?
- The Meaning of “Has” and “Have”
- Contractions with “Has” and “Have”
- How to Practice “Has” and “Have”
- Summary: “Has” vs. “Have”
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
“Has” vs. “Have”: What’s the Difference?
“Has” and “have” are both conjugations of the verb “to have.”
The main difference between them is that “has” is used with the third person singular (he, she, it), while “have” is used for all other subjects. The exception to this is with negative statements and questions, where you always use “have.”
You can think of the difference as being all about points of view.
In English, anything we read or speak is coming from a particular point of view. The point of view tells you who is speaking, and who is being spoken about.
You can know the point of view by looking at which pronouns are used. Let’s quickly review:
| Point of View | Meaning | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Person | The speaker is talking about himself or herself (with other people included if plural). | I have | We have |
| Second Person | The speaker is talking directly to somebody else. | You have | You have |
| Third Person | The speaker is talking about somebody or something else. | He has She has It has | They have |
Got it? Great! Now that you understand points of view, using “has” and “have” becomes very easy.
In the Present Tense
“Have” and “has” can both be used in the present tense as a main verb to mean possession.
Here’s the difference:
| Type of Sentence | Has | Have |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative Statement | ✓ (he, she, it, singular nouns) | ✓ (I, we, you, plural nouns) |
| Negative Statement | 𐄂 | ✓ |
| Question | 𐄂 | ✓ |
In the present tense, “has” is used with the third-person singular point of view. That means you’ll use it with “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
It’s also used with singular English pronouns like “everybody,” “anybody,” or “nobody”:
Everybody has a copy of the book.
Nobody has the answer.
I don’t think anybody has coffee.
“Have” is used for the other points of view–the first- and second-person points of view, and the third-person plural point of view.
In other words, use “have” with the subjects “I,” “you,” “we” or “they”:
I have a headache.
You have a new laptop.
They have three cats.
We have a big house.
Also, use “have” with plural nouns or when talking about multiple people or things at the same time:
Those dresses have stripes.
Roger and I have a red car.
My dog and Patricia’s cat have brown fur.
Aside from this, with negative statements or questions, you can only use “have” and not “has.” Even if the subject is “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun, you’ll need to use “have.”
Here are some questions in the present tense, all using “have”:
Does anybody have the answer to the question?
Do you have the book?
Does she have a house?
The same is true for negative statements in the present tense:
She does not have a room.
I do not have a brother.
They do not have time to see you.
In the Present Perfect Tense
“Has” and “have” can also be auxiliary verbs that help create the present perfect tense, in combination with other verbs.
The rules for using them as auxiliary verbs are actually simpler. It just depends on the subject.
If the subject is third-person singular: “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun, you’ll always use “has”:
John has gone to California four times.
The dog has not eaten today.
Has she received the letter?
You’ll use “have” in the present perfect tense with subjects “I,” “you,” “we” or “they,” as well as plural nouns.
I have watched “Game of Thrones” four times.
You have helped me a lot.
They have asked many questions.
We have thought about this all day.
This is true for negative statements or questions too:
My friends have not watched “Game of Thrones.”
You have not helped me at all.
Have they asked too many questions?
The Meaning of “Has” and “Have”
Now that you know about the differences between “has” and “have,” let’s review the two main uses of the verb “to have,” which is their infinitive, or original, form:
To Mean Possession
We use “to have” when we talk about possessing (owning) something.
Here are some conjugations of the verb “to have”:
| Tense | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Present | has, have |
| Present progressive | is / are having |
| Past | had |
For example, look at the following sentences:
She has the book.
I have the book.
In both sentences, the verb “to have” is conjugated in the present tense.
As Auxiliary Verbs
The verb “to have” has another use. It’s also an auxiliary verb.
An auxiliary verb is combined with another verb to complete the meaning of a sentence. Because of this, it’s also called a “helping verb.” For example:
She has eaten dinner already.
I have seen that movie.
These sentences both use the perfect tense. Here, “has” and “have” don’t indicate possession. Instead, adding “has” or “have” to another verb creates that verb’s perfect tense form.
In general, the verb “to have” is important as an auxiliary verb because it creates the past perfect and present perfect tenses for other verbs.
Contractions with “Has” and “Have”
In English, “has” and “have” are often used in contractions—which is where you combine two words with an apostrophe, and at least one letter is removed.
Contractions are incredibly common in informal English, whether in writing or speaking. For more formal types of writing, though, such as academic or business writing, contractions are often avoided, so you spell the words out instead.
Below are some examples of contractions combining “has” or “have” with personal pronouns and other common words, and you can click here for our full post on the topic.
| Original | Contraction |
|---|---|
| I have | I've |
| We have | We've |
| You have | You've |
| He has | He's |
| She has | She's |
| It has | It's |
| They have | They've |
| Should have | Hasn't |
| Would have | Haven't |
| Where has | Where's |
| Where have | Where've |
“Has” or “have” can also be combined with “not”:
| Original | Contraction |
|---|---|
| Has not | Hasn't |
| Have not | Haven't |
How to Practice “Has” and “Have”
Practicing English grammar doesn’t need to be hard or boring. There are many amazing resources available on the internet, plus other fun ways to practice.
- Take online quizzes. Try this quiz on EnglishGrammar and this one on EnglishExercises. For on-the-go practice, check out this worksheet from Study.com.
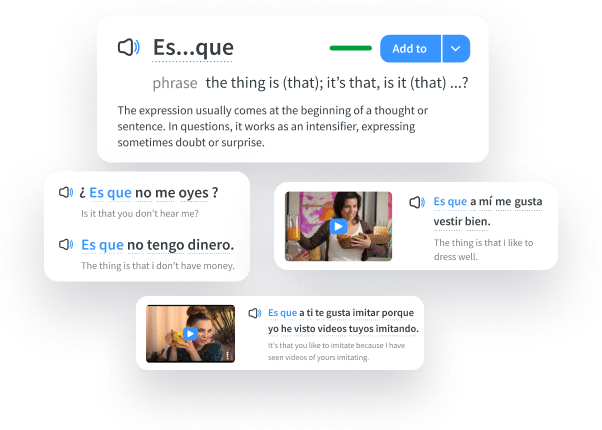
- Watch authentic English videos. Think of something you’re interested in, and find English videos about it—you’ll hear “has” and “have” quite frequently! For example, the language learning program FluentU has a large library of short English videos for different learner levels.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
- Try changing the pronouns in this article’s example sentences. This can be a good warm-up exercise. Once you’ve changed the pronouns, change the verb to match.
- Write a paragraph from multiple points of view. Try writing about yourself, and use the verb “have” as many times as you can. Then, rewrite the paragraph as though it’s about somebody else. This will force you to practice the difference between “has” and “have.”
Summary: “Has” vs. “Have”
“Have” and “has” are both conjugations of the verb “to have” in the present tense. “To have” is often associated with possession or ownership, but it can also be used as auxiliary (helping) verbs in the present perfect tense.
Either way, whether in the present or perfect tense…
- Use “has” with the subjects “he,” “she,” “it,” a name or a singular noun.
- Use “have” with the subjects “I,” “you,” “they,” “we,” a plural noun or multiple subjects.
An exception to this would be if you’re making a question or negative statement in the present tense. In that case, you’ll always use “have.”
Now, it’s time to use these important words.
Study all the examples closely. Use “has” and “have” in your daily conversations, and don’t be afraid of making mistakes!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
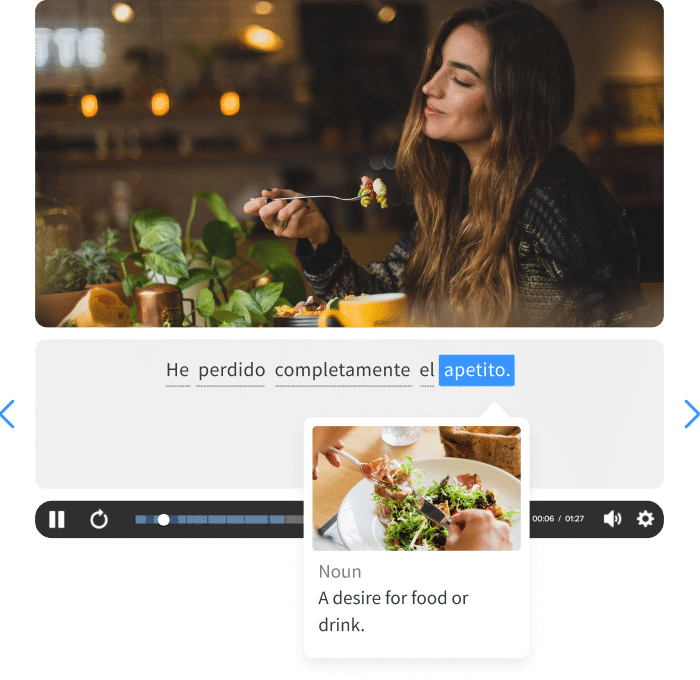
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
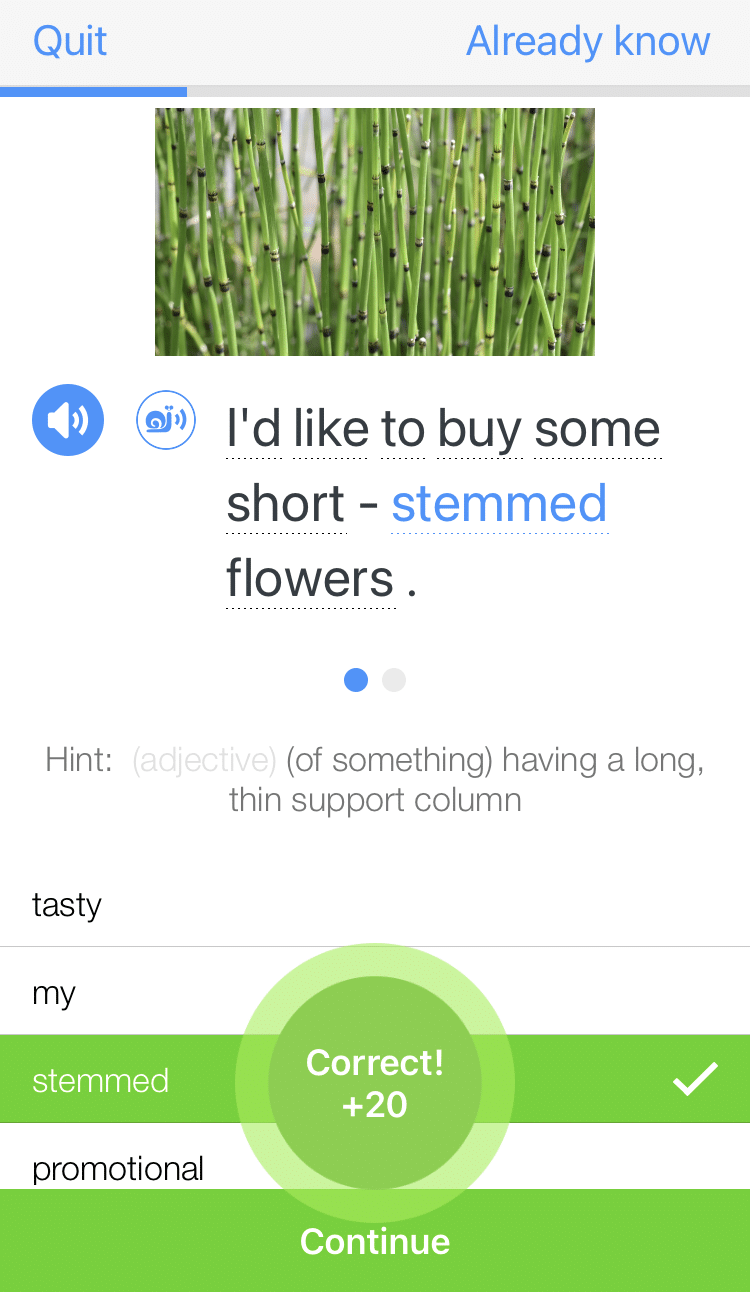
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)