The English Present Tense: Your Essential Guide
To speak about your likes and dislikes, hobbies and beliefs, you need to know one very important thing: the present tense.
Even if you can speak in present tense and read present tense, you may need to learn more about the details.
Here, you will learn everything you need to know.
Contents
- What Is the Present Tense?
- Using the Present Simple and Continuous Tenses
- Using the Present Perfect Tenses
- Telling Time with Present Tense
- Summary of the Present Tense
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What Is the Present Tense?
In English, a tense is how your listener knows what time you’re talking about.
A tense tells you when an action occurred.
The word even comes from an old Latin word that means time: tempus.
We use different forms of verbs—or action words—whether we’re talking about something that happened already, something that is happening now or something that will happen in the future. Using the right tense is important since it can help prevent misunderstandings.
The present tense is used for actions that are happening now, or that include what is happening now.
In this guide, we’ll explore all the different ways the present tense can be used in English.
Present Tense Forms in English
There are four forms of the present tense: simple, continuous, perfect simple and perfect continuous.
| Present Tense | When to Use | Structure | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | General or repeated actions | I/we/they + unchanged verb | I speak, they walk, we wish. |
| He/she/it + verb with -s at the end | He speaks, she walks. | ||
| Continuous | Ongoing actions | I am + verb with -ing at the end | I am running, I am speaking. |
| He/she/it is + verb with -ing at the end | He is eating, she is smiling. | ||
| We/they/you are + verb with -ing at the end | We are waving, they are talking, you are driving. | ||
| Perfect simple | Completed actions, with a connection to the present | I/we/you/they have + past participle | I have seen, they have arrived, we have finished. |
| He/she/it has + past participle | He has eaten, she has read, it has happened. | ||
| Perfect continuous | Actions that started in the past and continue in the present | I/we/you/they have been + verb with -ing at the end | I have been working, they have been studying, we have been waiting. |
| He/she/it has been + verb with -ing at the end | He has been running, she has been sleeping, it has been raining. |
When we talk about the English present tense, the main ones you need to know about are the simple and continuous tenses. These are straightforward and talk about actions that are regular (simple) or currently happening (continuous).
The two present perfect tenses (perfect simple and perfect continuous) connect past events to the present. These past events might be relevant to the present (perfect simple), or they’re still ongoing (perfect continuous).
As is true in many cases, there are exceptions (special cases that are different) to the rules.
There are some irregular verbs that look different in the present tense.
To have, to be, to go and to do are the biggest examples of irregular verbs. You will need to learn the rest, of course, but don’t worry. First, focus on learning the most common verbs.
All of this gets easier as you practice.
To start practicing, we will explore the different ways you can use these different types of present tense.
Using the Present Simple and Continuous Tenses
The present tense is all about what is happening now.
But it is also the right tense to use if you want to share your beliefs, general ideas, hobbies, things that happen more than once and a few other ideas like these.
Below you’ll learn how to talk about some of these things.
Generalizations and Beliefs
Saying something is general means it is not specific.
You are being specific if you say “I will eat fish today at 5:00.”
You can be general by saying “I eat fish.”
The second sentence describes a generalization, or something that is a big, non-specific statement. You use the simple present tense for this kind of speaking.
This way, you can share ideas, beliefs that you have, general facts or thoughts about yourself or others.
If you continue describing your love of fish to someone, you can tell them “fried fish smells delicious,” or “fish is the best food in the world.”
Notice that what you say doesn’t have to be true, it is just an idea or a belief.
Hobbies and Habits
What do you like to do in your spare time? The simple present tense can help you answer this question.
“I play the piano, and sometimes I read bad romance novels before bed.” You can be as general or specific as you want with your hobbies. Do you practice the piano for three hours every day? Do you go to sleep with your nose in a book? You can use the present tense to tell someone about that.
Hobbies are things that you do for fun. Habits, on the other hand, are things that you do sometimes without choosing to, and sometimes to make your life better (or worse).
You can have good habits: “I always wake up early and exercise before I start the day.”
You can also have bad habits: “When I’m nervous, I bite my nails. When I’m very nervous I make bad fish jokes.”
Both hobbies and habits are general descriptions of things that someone does. They might not be happening right at this moment (you’re not playing the piano and biting your nails as you read this) but they are said in the present tense because they are actions that include the current time.
How Often Things Happen
You might have noticed by now that the present tense is used to describe things that keep happening. You can also use the present tense to explain how often these things happen.
For example, if you say “He always drinks coffee in the morning,” it is not the same as saying “He never drinks coffee in the morning.” In fact, these two sentences have opposite meanings.
There are actually two time-related phrases in these sentences: (1) the words always and never explain how often your friend drinks coffee, and (2) the words in the morning explain when exactly this drinking happens (or doesn’t happen).
When you’re describing the frequency of an action (how often something happens), you can be very specific.
For example: “Every evening at 7:00 I study English for two hours.” This sentence tells when (7:00 in the evening), how often (every evening) and for how long (two hours) you study English.
Or you can be very general:
“Sometimes I study English.” This sentence only shows how often you study (sometimes).
What Is Happening Now
What are you doing right now? Maybe you are reading this article, drinking some tea and listening to some good music.
Anything that is happening right at this moment can be expressed with the continuous present tense.
Think of this as the way to express an action that hasn’t ended yet.
For example: “I am still waiting for this long winter to end.” If the winter was already over, this sentence would not be in the present tense! It would be in the past tense.
Scheduled Events
We keep saying that the present is something that happens now. However, you can also use it for scheduled events.
If your friend is coming to visit, you might say: “Annie’s train leaves New York today. She arrives here tomorrow at five.”
You use the present tense here because some preparation for this event has already happened. The simple present tense is usually used for events that are on a timetable or schedule or are happening very soon.
You can use the continuous present tense to say the same thing: “Annie’s train is leaving New York today. She is arriving here tomorrow at five.”
There is no difference between the two tenses in this case, so use whichever tense you’re more comfortable with!
Using the Present Perfect Tenses
The present perfect tenses are formed with has or have (depending on whether the subject is singular or plural) plus the main verb, and they’re used a bit differently:
Past Actions that Affect the Present
You might be used to thinking of the present tense as being used for actions that are happening right now or regularly. But the present perfect tense is mainly used for past events that are relevant to the present.
For example: “I’ve finished my report.” This statement means that you’ve already finished doing your report in the past, and this is relevant to the present—maybe you’re ready to submit your report now, or you already have time to do other things.
Here are other sentences with the present perfect: “They haven’t cooked dinner yet” or “She has bought a new laptop.”
If an event just happened, you can also use the present perfect tense for that. Remember to combine it with an adverb of time, like just, recently, or lately: “I’ve just finished watching the movie.” “I’ve recently visited that coffee shop.”
Experiences
Another function of the present perfect tense is to talk about experiences: “I have gone to Japan two times.” “I’ve taken guitar lessons.”
These are experiences that you’ve had in the past, and now they’ve added to your perspective of the world or affected how you are in the present.
The present perfect tense can also describe experiences that you haven’t tried. Just use its negative form, like in “I’ve never used a dating app before” and “I’ve never gone sky-diving.”
Past Actions that are Ongoing
If something happened in the past and you want to emphasize that it’s still happening now, then that’s where the present perfect continuous tense comes in.
For example, you can say: “I’ve been studying English for six years.” This means that you started studying English in the past, and until now you’re continuing to study it. Sometimes you can also remove the time reference: “She has been going to the gym.”
In some situations (but less commonly), the present perfect tense works for this too: “I’ve worked in this company since May last year” or “I’ve lived here for six months.” This usually includes since or for followed by the time duration.
Telling Time with Present Tense
As we mentioned before, English tenses tell you when something happens.
But these tenses alone don’t provide much information. When used alone, without any extra words to help the description, a tense can only tell you that the action happened now, happened before or has not happened yet.
Many times, you want to get information that is more specific than that.
To do that, you can add special time-related words that answer these questions:
- How long does the action happen for?
- How often does the action take place?
- When does the action happen?
Some examples of these time-telling words are:
- How long: All day, for hours, since this morning
- How often: Never, always, constantly
- When: Today, last year, at 5 in the afternoon
There are many more words that help describe the time of an action. Can you think of a few more?
Summary of the Present Tense
You should now have a good idea of when to use the present tense. Here’s a summary of what you learned in this article:
| Type of Present Tense | Uses | |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Generalizations and beliefs | Actions happening in the near future |
| Hobbies and habits | Scheduled events | |
| Frequency of an action | ||
| Present Continuous | Actions happening right now | |
| Present Perfect Simple | Past actions that affect the present | Duration of an ongoing past action |
| Recent events | ||
| Experiences | ||
| Present Perfect Continuous | Past actions that are still ongoing | |
How well did you understand how to use the present tense?
Now that you’ve read this guide, you can try testing yourself.
You can find some present tense exercises on the English Page website, or choose from a large selection of exercises on this German English-learning website.
But don’t just memorize grammar rules and do practice exercises to master the present tense: make sure you have lots of authentic English audio and video to help you listen to the English present tense in context.
When you read English books, listen to English podcasts and music or watch English videos, look carefully for the present tense. Study why or how certain phrases use the present tense, paying attention to the conjugated verbs and the words that follow it.
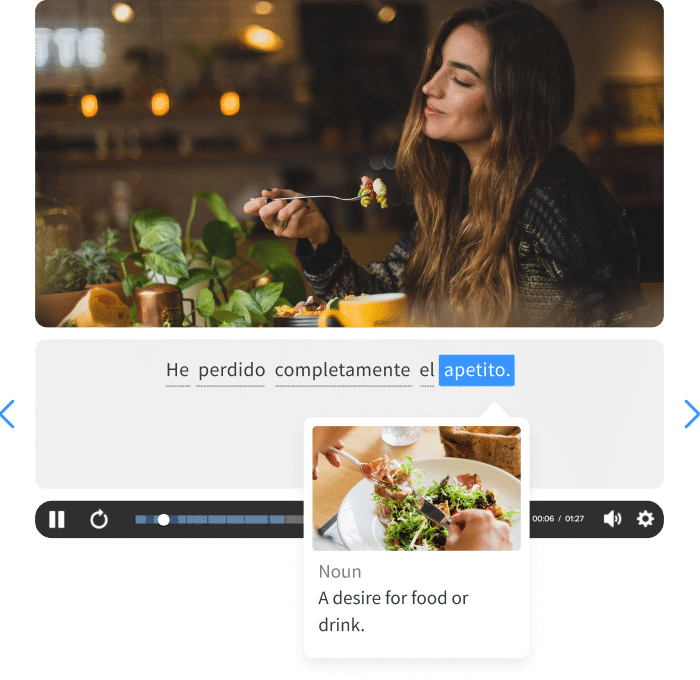
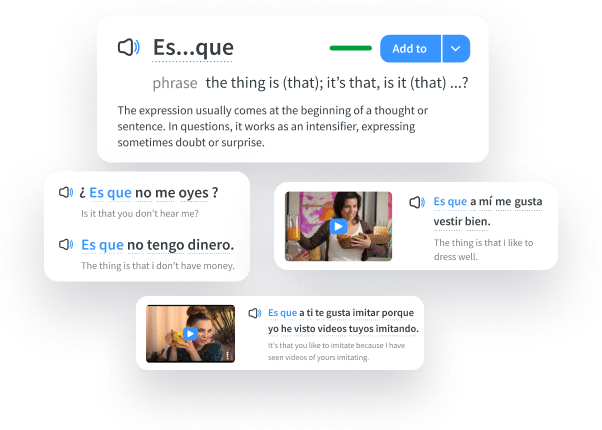
Some language learning programs can also show when the present tense is expected to be used. FluentU, for example, uses authentic English videos so that you can learn vocabulary and sentence structure in context. Each video has interactive subtitles that provide word definitions and grammar details, so you can easily see and study instances of the present tense.
Now go out there and try your new skills in the real world!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)