120+ Car Parts in English
English is spoken in more than 70 countries around the world.
Simply land in your English-speaking country of choice and choose from one of many car rental companies at the airport and go adventuring!
But what happens if something goes wrong and you need help?
Check out this ultimate guide to more than 120 car parts, car-related vocabulary and driving verbs in English, and you’ll be cruising confidently on the open road in no time.
Contents
- Exterior (Outside) of the Car
-
- 1. Headlights
- 2. Taillights
- 3. Signal lights / Blinkers / Turn Signals
- 4. Emergency Lights / Hazard Lights
- 5. Bumper
- 6. Exhaust Pipe / Tailpipe
- 7. Side View Mirrors
- 8. Rearview Mirror
- 9. Windshield / Windscreen
- 10. Windshield Wipers / Windscreen Wipers
- 11. Engine
- 12. Trunk / Boot
- 13. Hood / Bonnet
- 14. Fender
- 15. Sunroof
- 16. Rims
- 17. Fuel Tank
- Interior (Inside) of the Car
- Additional Car-related Vocabulary in English
- Common Issues with Cars and Their Solutions in English
- How to Practice Car Parts in English
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Exterior (Outside) of the Car
1. Headlights
These are the lights at the front of the car that let you see where you’re going. There are two of them; one on the driver’s side and one on the passenger’s side.
When most cars are started, the running lights (low brightness safety lights on the front of the car) are automatically turned on. Headlights can be turned on at night or when it’s a little dark out, such as during a storm.
2. Taillights
These are the lights at the back of the car that let drivers behind you know when you’re braking (stopping). There are also two of these; one on each side of the car.
3. Signal lights / Blinkers / Turn Signals
These are the lights at the front and back of the car that let drivers know which way you’re going to turn. There are two sets; one on the right side for turning right, and one on the left side for turning left.
4. Emergency Lights / Hazard Lights
These lights use the same light bulbs as the signal lights. In an emergency (when something bad suddenly happens), the emergency lights can be switched on to let other drivers know there’s a problem and to give you space.
5. Bumper
This is a piece of metal that goes across the whole front of the car. It’s there to minimize (lessen) damage if the car hits something head-on.
6. Exhaust Pipe / Tailpipe
This is where exhaust (burned fuel) from the engine exits the car while it’s running.
7. Side View Mirrors
These are small mirrors on either side of the car beside the front windows that allow the driver to better see around the car while driving.
8. Rearview Mirror
This is the mirror at the top of the windshield (see definition below) that allows the driver to see behind them while driving without having to turn and look back.
9. Windshield / Windscreen
This is the giant pane of glass at the front of the car.
10. Windshield Wipers / Windscreen Wipers
These are the blades that remove water from or clean dirt off the windshield. They can be turned on when it’s raining, or they can be used with windshield wiper fluid (liquid that can be bought to clean the windshield).
11. Engine
This is the central part of the car. An engine is a machine with multiple parts that makes the car work.
12. Trunk / Boot
This is the compartment (the closed space) in the back of the car that can be used for storage. Sometimes a spare (extra) tire can be found here. In many parts of the world, the trunk is also called the boot.
13. Hood / Bonnet
This is the front of the car where the engine and other car machinery can be found. There’s a lever (a rod) in the car to lift the hood (open the hood of the car) to allow access to what’s underneath.
14. Fender
This is the area around the car’s wheels that keeps it protected and from getting debris (garbage, rocks or rubble) inside the wheel well. This is sometimes called the mudguard.
15. Sunroof
Not all cars have a sunroof. This is a small window on the roof of the car that allows the driver and passengers to look up at the sky or let the sunshine in.
16. Rims
These are the outer shells of the wheel, often placed over the bolts that hold the wheels to the car. Not all cars have them, and they can be very decorative. These are sometimes called hubcaps.
17. Fuel Tank
This is the place where the gasoline goes. There’s a small hatch (door) on the side of the car that leads to where you put the nozzle in to fill the car with gas.
Interior (Inside) of the Car
18. Steering Wheel
This is the part in front of the driver’s seat that allows the driver to control the direction of the car.
19. Battery
This is the object that powers all the car’s electronic features and the motor. It can be found under the hood of the car.
20. Radio
Powered by the battery, the radio allows the driver to listen to music or news while driving. The settings for this can be found in the car’s dashboard (the front inside of the car that the driver can access) to the right of the steering wheel.
21. Stick Shift / Gear Shift
If the car is manual, that means that the driver must change the car into different gears (adjust the engine depending on speed). For this, the driver can use the stick shift.
For automatic cars, the car changes into different gears on its own. In these cars, the stick shift is used to put the car in the drive, reverse, neutral or park.
22. Speedometer
This gauge (dial) is on the dashboard and allows the driver to see how fast they’re going.
23. Ignition
This is the place beside the steering wheel where the car key can turn on the car. When the car key is put into the ignition and turned, the battery and engine turn on.
24. Air Bag
If the car gets into an accident, rapidly (very fast) inflating sacs (bags) of air pop out of the steering wheel and front interior (inside) of the car to stop the driver and passengers from being thrown further forward and seriously hurting themselves.
25. Fuse Box
Underneath the dashboard (typically under the steering wheel), there’s a panel that can be removed to expose the fuse box. This is where the control board of the electrical system is located.
26. Brake
This is the pedal to the left side that stops the car when in motion.
27. Accelerator
The accelerator is the pedal to the right side that makes the car move. The harder you press, the faster the car accelerates (moves forward).
28. Radiator
Underneath the hood, there’s a water tank called the radiator. It’s responsible for cooling the engine, so the car doesn’t overheat (get too hot).
29. Fuel Injector
Under the hood of the car, this piece of machinery delivers the gas into the engine so that the car can use that fuel to move.
Additional Car-related Vocabulary in English

- Alignment — The proper adjustment of various components, such as wheels, suspension, etc., to ensure they work together correctly.
- Alternator — A device in a vehicle that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, which charges the battery.
- Axle — A shaft on which wheels rotate; it may be fixed to the wheels or rotate with them.
- Carburetor — A device that blends air and fuel for an internal combustion engine.
- Chassis — The framework of a vehicle, which supports the body and other components.
- Clutch — A mechanism that engages and disengages power transmission, usually between the engine and gearbox.
- Crankshaft — A shaft with one or more cranks, connected to pistons in an engine, which converts linear motion into rotational motion.
- Cylinder — A chamber within an engine in which a piston moves.
- Dashboard — The panel in front of the driver, containing various controls and indicators.
- Drive Shaft — A mechanical component that transmits power from the engine to the wheels.
- Exhaust — The system that carries waste gases away from the engine and disposes of them.
- Filter — A device that removes impurities or unwanted substances from a fluid or gas.
- Fuel — A substance burned to produce energy, especially for vehicles.
- Gearbox — The assembly of gears through which power is transmitted from the engine to the wheels.
- Gasket — A mechanical seal that fills the space between two or more mating surfaces to prevent leakage.
- Headlight — A powerful light at the front of a vehicle used for illumination.
- Indicator — A flashing light on a vehicle that indicates a change in direction.
- Car Key — The special key you use to unlock and start the car.
- Satellite Navigation — The system in your car that tells you directions.
- Power Windows — Windows that go down by pushing a button on the car door.
- Remote Key Fob — The small fob with buttons that unlocks, and sometimes starts the car.
- Car Seat — The seat you strap into the back seat to hold small children.
- Jack — A device used to lift a vehicle off the ground to facilitate maintenance or repair.
- Muffler — A device that reduces the noise emitted by the exhaust of an internal combustion engine.
- Odometer — A device that measures the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- Oil — A lubricating substance used in engines to reduce friction and wear.
- Piston — A component in an engine that moves back and forth within a cylinder.
- Seat Belt — A safety belt designed to secure occupants in a vehicle.
- Shock Absorber — A device that absorbs and dampens shock impulses in a vehicle’s suspension system.
- Spark Plug — A component that ignites the air-fuel mixture in an internal combustion engine.
- Starter — A device that initiates the engine’s operation.
- Steering Wheel — The wheel used to control the direction of a vehicle.
- Suspension — The system of springs, shock absorbers, and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels.
- Tailpipe — The pipe through which exhaust gases are emitted from a vehicle.
- Throttle — A valve that regulates the flow of air or fuel in an engine.
- Tire — A rubber covering around a wheel.
- Transmission — The mechanism that transmits power from the engine to the wheels.
- Turbocharger — A device that compresses the air entering the engine, increasing power.
- Valve — A device that controls the flow of gases or liquids.
- Windshield Washer — A device that sprays liquid onto a surface to clean it.
- Wheel — A circular object that revolves on an axle.
- Air Filter — A device that removes particulates from the air before it enters an engine.
- Antifreeze — A liquid used in a vehicle’s cooling system to prevent freezing.
- Camshaft — A shaft with lobes that open and close the valves in an engine.
- Catalytic Converter — A device that converts harmful gases from the exhaust into less harmful substances.
- Clutch Cable — A cable that engages and disengages the clutch in a manual transmission.
- Cruise Control — A system that automatically controls the speed of a vehicle.
- Distributor — A component that routes electrical power from the ignition coil to the spark plugs.
- Exhaust Manifold — A series of pipes that collect exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders.
- Fuel Pump — A device that delivers fuel to the engine.
- Glove Compartment — A small storage compartment in the dashboard.
- Heater — A device that warms the interior of a vehicle.
- Horn — A device that produces a loud sound to warn others.
- Hubcap — A decorative cover for a wheel’s hub.
- Ignition Coil — A component that transforms low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to ignite the fuel.
- Intake Valve — A valve that allows the mixture of air and fuel to enter the combustion chamber.
- Lug Nut — A nut used to secure a wheel to its hub.
- Mirror — A reflective surface used to see behind or around a vehicle.
- Piston Ring — A ring that seals the gap between a piston and a cylinder.
- Power Steering — A system that assists in steering a vehicle.
- Radiator Fan — A fan that draws air through the radiator to cool the engine.
- Radiator Hose — A hose that carries coolant between the engine and radiator.
- Shock Absorber — A device that absorbs and dampens shock impulses in a vehicle’s suspension system.
- Spare Tire — An extra tire carried in a vehicle for emergencies.
- Wheel Well — The area around a wheel where the fender is located.
- Accelerate — To increase the speed of a vehicle.
- Brake — To slow down or stop a vehicle using the brakes.
- Steer — To control the direction of a vehicle.
- Turn — To change the direction of a vehicle.
- Park — To bring a vehicle to a stop and leave it in a particular place.
- Reverse — To drive a vehicle backward.
- Merge — To combine two lanes of traffic into one.
- Signal — To indicate a turn or lane change using lights or signals.
- Navigate — To find the correct route and direction while driving.
- Idle — To run an engine at low speed without moving.
- Cruise — To maintain a steady speed while driving.
- Overtake — To pass another vehicle traveling in the same direction.
Common Issues with Cars and Their Solutions in English
Now that you know some common car parts in English, you should also know some common car problems as well as what to do when these problems happen.
A warning light has come on in my car
Solution: A warning light (a bright light on the dashboard) is often the first sign of trouble in a car, but there’s no need to panic.
Warning lights can be a check engine light that means the engine should be inspected, a low fuel light that means you need to put gas into the car or a change oil light that means you need to change the engine oil.
Be sure to check your owner’s or renter’s manual to figure out what the warning light means. You can solve the problem yourself if it’s possible or take your car to a mechanic (someone who fixes cars) to find out what’s wrong and get further assistance (help).
My car has a flat tire
Solution: Many things can cause flat tires (tires that have low or no air in them).
Sometimes a tire is just low on air. In this case, take the car to a gas station (the place to buy gas for the car) to get more air. Often, however, the tire has been punctured (stabbed) by a nail or some other sharp object.
If the car has a spare tire, you can install the spare yourself. You should later bring the car with the flat tire to the mechanic to have the tire patched (fixed) or replaced.
My car won’t start
Solution: If you put the key into the ignition, turn it and nothing happens, the reason could be a number of things. First, you should try jumping the car’s battery (using power from another car to recharge the battery of your car) with jumper cables.
If the car is still not starting, call a tow truck (a pick-up truck that can pull cars) to bring your car to the mechanic for further assistance.
My car’s engine is overheating, and there’s steam coming from under the hood
Solution: This is a serious problem and could be very dangerous. If you see smoke coming out of the front of your car, it’s probably overheated. Pull over immediately and turn the car off. Next, call a tow truck and bring the car to a mechanic.
I’ve gotten into a car accident
Solution: This is perhaps the most stressful situation for those driving a car in a foreign country.
First of all, make sure everyone involved is okay, and make sure to get out of the way of traffic, so further collisions (accidents) don’t occur. Call an ambulance if medical assistance is necessary.
If you’re renting the car, you should call the rental company immediately (right away) for instructions. You should also exchange information (name, phone number, insurance, etc.) with the other driver. This may be needed later.
If someone is seriously injured or the car cannot be driven because it’s totaled (destroyed), call the authorities (police), as well. In many places, it’s illegal to leave the scene of an accident, so make sure you follow all the steps before leaving, no matter how small the accident may seem.
How to Practice Car Parts in English
Cars can be tricky—some take synthetic oil, some take premium gas and some have stick shifts.
With all these advanced terms, you’re going to need to practice!
One of the easiest ways to practice car parts in English is by looking at your car manual (the book that explains how the car works). By law in most countries around the world, a car must be sold with its matching manual to aid with any maintenance (work that keeps the car running safely and without problems) or repairs.
If you have a car, chances are that car has a manual in its glove compartment (the closed space under the dashboard of the passenger side).
Best of all, many car manuals are in multiple languages. That means that you’ll be able to find the manual in your native language as well as in a foreign language. If your car manual has a translation in English—that’s awesome! You can study the manual in English using the text in your native language as a reference.
You can also apply your new knowledge of car parts in English by actually labeling a car on Passport to English.
You can create flashcards using multimedia related to cars with the FluentU program to further practice your new vocabulary.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
More quizzes for the names and definitions of car parts can be found at Grizly, as well as Quizizz.
Furthermore, the ISL Collective also offers long-answer questions for you to practice your knowledge of car-related situations.
Well, that should be enough to build your confidence a bit and make you feel more secure about driving in an English-speaking country.
So, put your luggage in the trunk and turn up your favorite tunes on the radio. Road-tripping is one of the best ways to explore the English-speaking world, and with your new knowledge of car parts in English, you’re ready to hit the open road!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
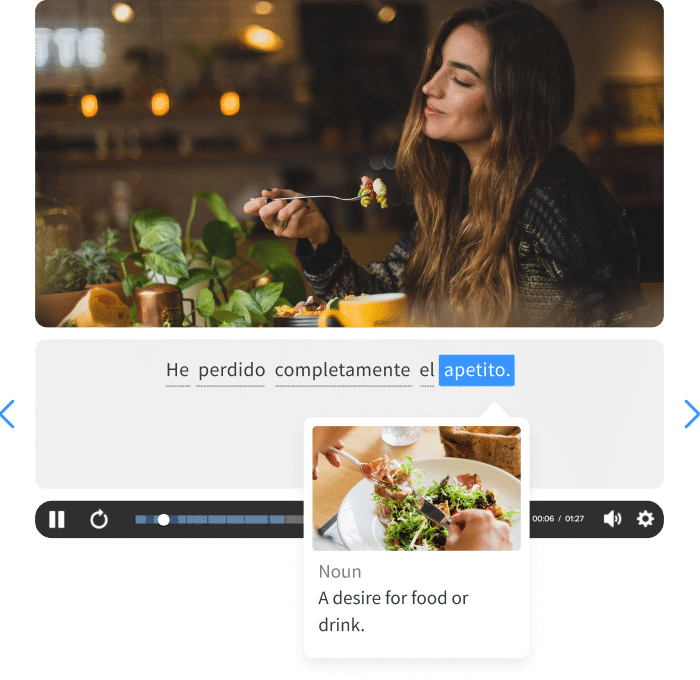
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
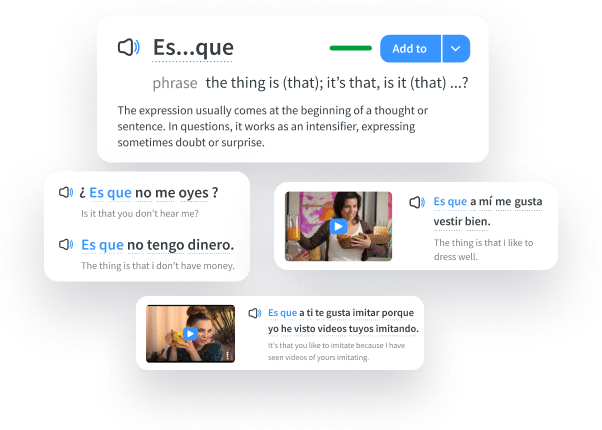
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)