160 English Nature Words
Are you a nature lover?
If you are, being able to talk about nature in English would certainly be beneficial.
Since there are over 160 nature words on this list, regardless of your language level, you’ll definitely pick up some beautiful nature vocabulary!
You’ll learn how to describe landscapes, weather conditions, various types of plants, geological features and climate change patterns.
Let’s get started!
Contents
- Words for Describing Geological Features
- Words for Weather Conditions
- Words for Plants, Flowers and Trees
- Words for Gardening Tools
- Words for Beautiful Landscapes
- Words for Ancient Geological Features
- Climate Change Vocabulary
- The Best Way to Practice Nature Words in English
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Words for Describing Geological Features
Geological features are landscape characteristics found in nature that are not plants or animals.
1. Lush
Used to describe plants and flowers that are healthy and growing well.
2. Grassy
Used to describe meadows and fields that have a lot of grass or green plants.
3. Floral
Used to describe gardens or landscapes that have a lot of flowers.
4. Vivid
Something that’s bright or colorful.
5. Abloom
Used to describe flowers or groups of flowers that are blooming.
6. Vibrant
Something that’s bright and eye-catching.
7. Dense
Used to describe plants that are growing close together and are hard to see through because they’re so thick.
8. Earthy
Something that contains or looks like soil or dirt.
9. Diversified
Used to describe a garden or landscape that has a lot of different plants.
10. Dry
Without water.
11. Bare
Without plants.
12. Dead
Used to describe plants that are no longer living.
13. Oversaturated
Used to describe plants that have had too much water or rain.
14. Flooded
Used to describe landscapes that are covered in water due to overflowing rivers or lakes.
15. Flowering
Used to describe when flowers first start appearing on plants.
16. Budding
Used to describe the first stage of flowering.
17. Hilly
A landscape containing a lot of hills.
18. Mountainous
A landscape containing lots of mountains.
19. Wavy
Used to describe water with rough waters.
20. Rolling
Used to describe a landscape with a lot of hills that resembles (looks like) ocean waves.
21. Stormy
Used to describe a lot of rain, lightning, thunder and wind.
22. Misty
A landscape that has a light haze of rain in the air; oceans and waterfalls often produce mist.
23. Frigid
Extremely cold.
24. Desolate
A bare landscape where few plants are growing.
25. Untouched
A landscape that has not been changed by human beings.
26. Pristine
A lush landscape that appears untouched or “picture-perfect.”
27. Tropical
Alandscape that’s warm with jungle plants and palm trees; common on islands near the equator.
28. Arid
A dry landscape that receives very little rain.
Words for Weather Conditions
29. Sunny
A lot of sunshine.
30. Humid
A lot of moisture in the air.
31. Stifling
So hot that one is uncomfortable.
32. Gloomy
Cloudy and gray weather.
33. Rainy
A lot of continuous (ongoing) rain.
34. Dry
Little to no rain.
35. Cloudy
A sky mostly covered in clouds.
36. Foggy
Used to describe a landscape with a lot of fog (a light cloud at the ground level.)
37. Clear
No clouds or rain.
38. Crisp
Describing a cool temperature.
39. Cool
Slightly cold or chilly.
40. Windy
A lot of wind.
41. Breezy
A similar meaning to windy, but a breeze is less strong than wind.
42. Wet
The landscape after a lot of rain.
43. Fair
Weather that’s clear and warm.
44. Mild
Pleasant or not too warm.
45. Still
No wind.
46. Overcast
A lot of clouds in the sky, but little to no rain.
Words for Plants, Flowers and Trees
Small and Skinny Plants
47. Bush
A plant that grows close to the ground; it expands widely and has leaves.
48. Shrub
Another word for bush.
49. Hedge
Similar to bush but often trimmed to be rectangle-like; these often surround houses or are used to create a boundary or fence.
50. Grass
A plant that grows widely in fields and meadows; it’s also common on household lawns.
51. Moss
A soft plant that grows on rocks and trees; it looks like a green carpet.
52. Mushroom
A fungus that grows in dark places; some can be eaten and others are poisonous.
53. Herb
A variety of plant that’s used for flavoring food (basil, cilantro, mint, etc.) or as medicine or tea.
54. Fern
An ancient (very old) plant whose leaves look like feathers.
55. Reed
A plant that looks like tall grass and grows in wetlands and swamps.
56. Bamboo
A plant that looks like long stalks of wood and grows in tropical places.
57. Ivy
A plant with five-pointed leaves that grows close to the ground and climbs trees and buildings.
58. Poison Ivy
A type of ivy that causes extreme itching and a rash, if touched.
Main Parts of Plants
59. Seed
What plants grow out from.
60. Root
The part of the plant that remains underground and absorbs water.
61. Stem
The part of the plant that grows upward and holds the flower up.
62. Stalk
Another word for a stem.
63. Leaf
The green part of the plant that absorbs sunlight.
64. Petal
The colorful parts of the flower.
65. Bud
The first stage of plant growth that’ll flower and bloom.
66. Thorn
A part on the stem of a flower or plant that’s prickly and sharp.
67. Branch
The part of the tree that grows out from the trunk.
68. Twig
A small branch.
69. Bark
The outer skin of a tree.
Pretty and Common Flowers
70. Daffodil
A flower with small yellow petals.
71. Rose
Flowers with thorns and bright red petals.
72. Dandelion
A weed that has yellow flowers.
73. Daisy
A flower that has white petals around a yellow top.
74. Lily
A medium-sized flower whose petals can be all different colors.
75. Tulip
Common in many gardens, and famous in Holland; they can be multiple colors and are associated with Easter.
76. Sunflower
A big flower with bright yellow petals and a brown center.
Now that you know all the basics, try practicing your plant vocabulary!
Typical Tall Trees
Two common types of trees are deciduous and evergreen.
Deciduous trees shed (get rid of) their leaves during a specific part of the year, typically autumn or fall, and evergreen trees keep their leaves all year.
Not all trees fall into these two categories though, as you’ll see in this shortlist.
77. Palm tree
(Neither deciduous or evergreen) a tropical tree with large, featherlike leaves and sometimes coconuts.
78. Cactus
(Neither deciduous or evergreen) a plant that grows in the desert with thorns or thistles (pointy, sharp spines.)
79. Maple
A deciduous tree with three-pointed leaves.
80. Oak
A deciduous tree with acorns.
81. Birch
A deciduous tree with thin, white bark.
82. Willow
A large deciduous tree with thin leaves and curtain-like branches.
83. Poplar
A medium-sized deciduous tree with teardrop-shaped leaves.
84. Pine
An evergreen tree with needle-like leaves and pinecones.
Words for Gardening Tools
85. Gardener
Someone who maintains a garden.
86. Flower pot
A container where one or more flowers grow.
87. Vegetable garden
A garden that specifically grows vegetables.
88. Weed
A plant in a garden that’s not desired.
89. To weed
(Action verb) to pick and remove the weeds from the garden.
90. Shovel
A tool used to dig in the ground.
91. Pail
A cylindrical (circular) container for carrying water.
92. Watering can
A container specifically used to water plants.
93. Shears
A tool used to cut through or trim plants.
94. Rake
A tool used to gather trimmed plants or fallen leaves from the ground.
95. Hoe
A single-bladed tool used to dig out weeds.
96. To sow
(Action verb) to plant seeds.
97. To mow
(Action verb) to trim the grass, often with a lawnmower.
98. Lawnmower
The machine used to mow the lawn; it can be gas-powered or hand-pushed.
99. Wheelbarrow
A single-wheeled cart for carrying gardening materials.
100. Shed
A small shelter in a yard that stores gardening materials or other outdoor objects and tools.
Words for Beautiful Landscapes
101. Bay
Where the sea curves inward to create a body of water with the coast on three sides.
102. Lake
A small body of water inland; lakes are often freshwater.
103. Sea
A large body of saltwater.
104. Ocean
A larger body of salt water; there are five oceans: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic and Southern.
105. River
A flowing stream of water.
106. Creek
A thin river.
107. Waterfall
When water falls from a higher point like a cliff to a lower point.
108. Canyon
An arid and rocky valley surrounded by cliffs.
109. Glacier
A large expanse (area) of ice around the polar regions of the Earth.
110. Meadow
A large field with grasses and flowers.
111. Forest
A landscape with dense plants and trees.
112. Mountain
A big elevation in the Earth; mountains are often rocky, snow-covered or volcanic.
113. Hill
A small elevation in the Earth.
114. Plain
A flat expanse of land; plains are often grassy.
115. Marsh
An expanse of land that regularly floods and remains saturated.
116. Island
An expanse of land surrounded by water on all sides.
117. Peninsula
An expanse of land surrounded by water on three sides.
118. Savanna
An arid field in a tropical region; there are a lot in Africa.
119. Valley
An expanse of land between mountains or hills.
120. Desert
A dry landscape often covered in sand or rocks; not many plants grow here.
121. Tundra
A dry landscape in cold climates.
122. Cliff
A steep mountain-like formation; these are common along coasts.
123. Cave
A tunnel or chamber underground.
124. Beach
A sandy expanse of land near bodies of water.
125. Field
An expanse of land where grasses and other plants are common.
Don’t forget to practice your landscape vocabulary!
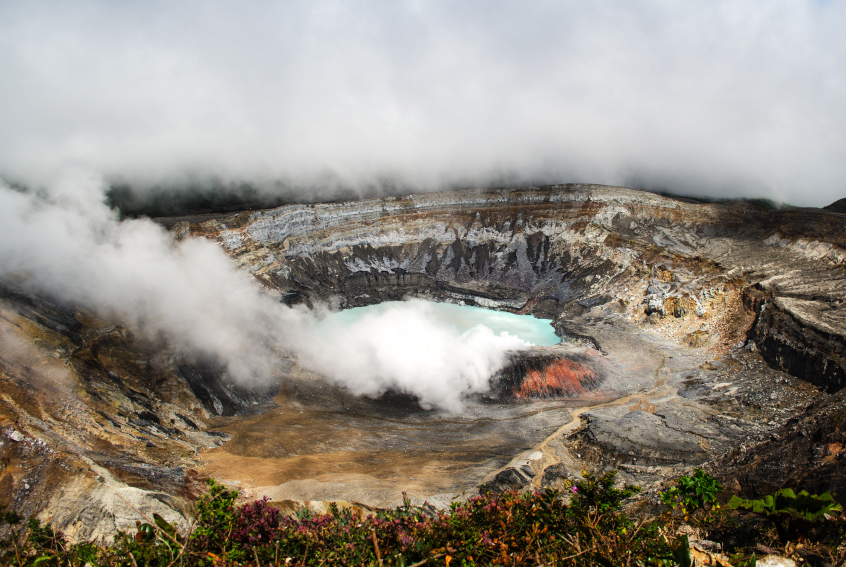
Words for Ancient Geological Features
The word geology is a noun that means the study of the Earth and its physical processes.
This list of vocabulary also has words that describe significant events that impact human activity and are caused by the Earth.
126. Bedrock
Large expanses of flat rocks.
127. Sedimentary rock
Rock that’s moved by water or wind.
128. Igneous rock
Rock that’s made directly from lava or magma.
129. Metamorphic rock
Sedimentary or igneous rocks changed by extreme heat.
130. Crater
A large, circular hole or indentation in the Earth; usually formed by a volcano.
131. Erosion
When water or air breaks away at rocks.
132. Fossil
Old remains from a plant or animal that died a long time ago.
133. Gem
A precious stone often used for jewelry.
134. Geyser
When hot water sprays up from under the Earth.
135. Hot spring
A pool where water is warmed by underground Earth processes.
136. Mineral
A solid material made by the Earth.
137. Seismic activity
The movement of the Earth’s plates created by natural processes.
138. Earthquake
When seismic plates shift, causing the Earth to shake and split.
139. Volcano
A mountain formed by eruptions and lava.
140. Magma
Hot fluid under the Earth.
141. Lava
When magma surfaces from underground.
142. Eruption
When lava or magma spews from the Earth at the top of a volcano.
143. Tsunami
A giant wave often caused by an underwater earthquake.
144. Fossil fuel
A natural fuel burned by humans to run things like cars, airplanes and electricity.
Climate Change Vocabulary
Climate change is a noun that describes global weather patterns and temperatures that have changed due to the impact of human activity.
145. Atmosphere
Layers of gases in the sky that encase the Earth.
146. Ozone
A layer of oxygen above the Earth that protects us from the sun.
147. Carbon dioxide
What we exhale when we breathe; we also create this by burning fossil fuels.
148. Emissions
These are produced when we burn fossil fuels; they commonly come out of cars, power plants and factories.
149. Ecosystems
A community of plants and animals that depend on each other for survival.
150. Habitat
A place where an animal lives.
151. Extinction
When all members of an animal species die.
152. The Greenhouse Effect
When emissions get stuck under the Earth’s atmosphere and warm the planet.
153. Pollutant
Something that pollutes or damages the Earth.
154. Non-renewable resource
A resource that can only be used once; an example would be natural gas.
155. Renewable resource
A resource that can be used over and over again; an example would be wind.
156. Coal
Ancient plant matter now in rock form that can be burned for fuel.
157. Oil
A liquid found in the Earth that can be burned for fuel.
158. Solar energy
A form of energy that uses the sun’s rays.
159. Wind energy
A form of energy that uses wind.
160. Drought
When a landscape is dry for an extended period of time.
161. Ice caps
Another word for glaciers in the polar regions of the Earth.
While some of these words are pretty complicated, practicing climate change vocabulary is important if you want to take about current events that involve the environment.
And if you’re up for a challenge, try practicing all of the nature words together!
The Best Way to Practice Nature Words in English
Long-term memory is where knowledge and vocabulary words stay for long periods.
That means that once a word is in your long-term memory, you should be able to use that word a week from now, a month from now or even a year from now.
To move words from your short-term memory to your long-term memory, you should make words meaningful for you.
- When learning a new word, try using it in a full sentence and write that sentence down in a notebook. In many cases, you can use several words that are related to each other to help you remember their meaning.
- To take your practice a step further, try going for a walk in nature. As you’re walking, create sentences and descriptions of what you’re seeing.
- Better yet, write these sentences down or bring a voice recorder with you! This is a great way to use nature words and record the descriptions you’re creating to review again later.
- Use a program like FluentU to learn nature words in context.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Your English nature word vocabulary is growing into quite a beautiful garden!
Take care of the seeds you just planted, and watch your nature vocabulary flourish!
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing...
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
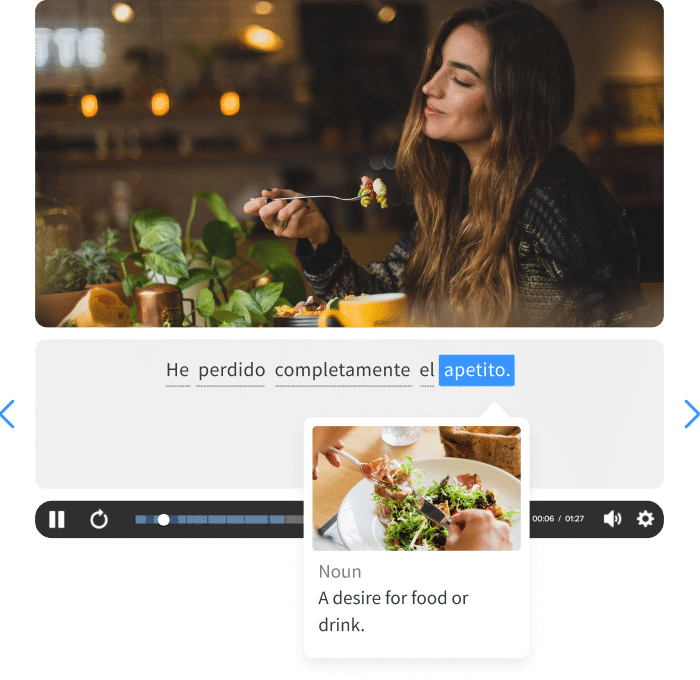
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
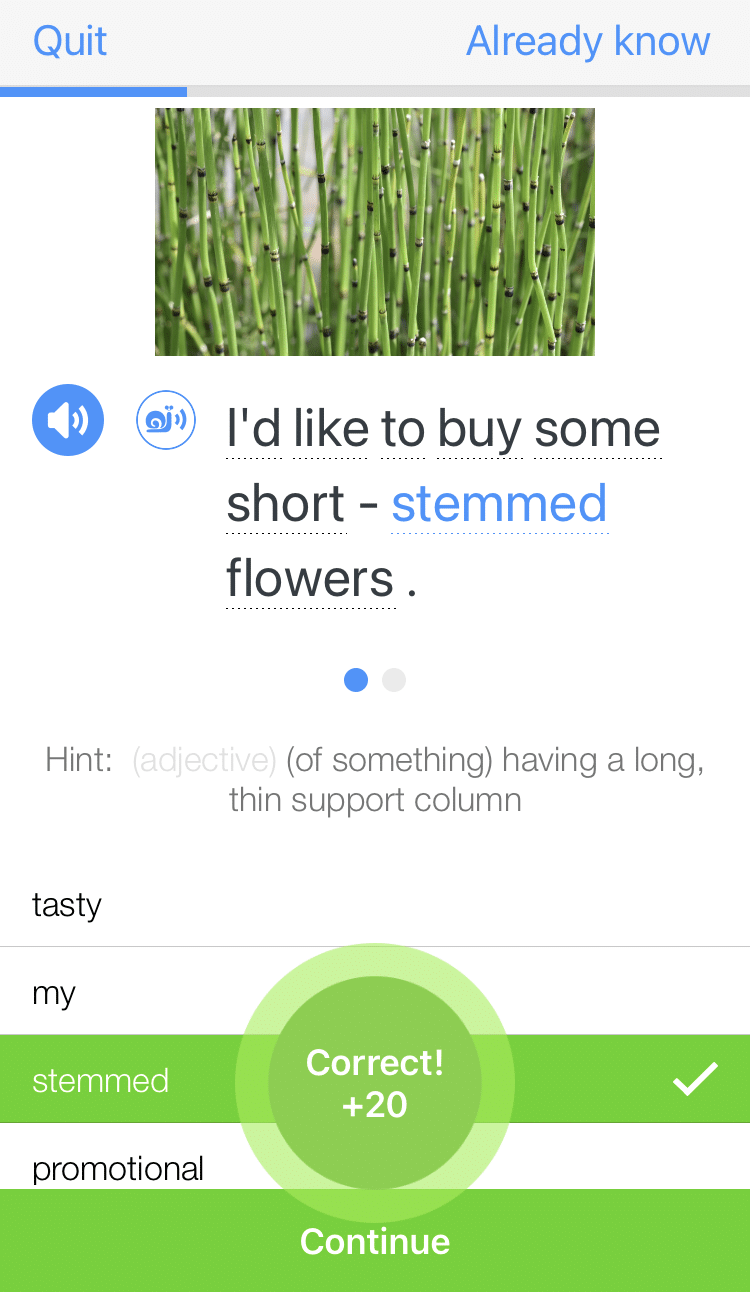
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)