9 Types of English Pronouns and How to Use Them
You might already know what a noun is, so the next step is to learn about pronouns. A pronoun in English can replace a noun or a noun phrase.
This means a pronoun can refer to a person, animal, object, place, thing or idea already mentioned before.
Learn everything you need to know about English pronouns, divided up into nine different pronoun types, with plenty of examples.
Contents
- What Are Pronouns in English?
- 1. Personal Pronouns
- 2. Possessive Pronouns
- 3. Demonstrative Pronouns
- 4. Indefinite Pronouns
- 5. Relative Pronouns
- 6. Interrogative Pronouns
- 7. Reflexive Pronouns
- 8. Reciprocal Pronouns
- 9. Intensive Pronouns
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What Are Pronouns in English?
A pronoun is a word that can substitute a noun or a noun phrase.
Consider these example sentences with nouns and pronouns:
| Sentence with noun | Sentence with pronoun |
|---|---|
| My mom loves animals. | She loves animals. |
| Your brother is very impatient. | He is very impatient. |
| This book is excellent. | It is excellent. |
This is just one type of pronoun—the personal one. English has a total of nine different types of pronouns, and each is used for different purposes.
1. Personal Pronouns
Despite the name, personal pronouns do not only refer to people. They can also substitute for animals and objects. Personal pronouns are probably the type of pronoun that you are most familiar with since they are taught very early on to beginner English learners.
This type of pronoun changes depending on:
- grammatical person (who you are talking about)
- gender (only in the third person singular)
- number (how many)
There are two kinds of personal pronouns, depending on their function in the sentence.
Subject Personal Pronouns
Subject personal pronouns function as subjects of sentences. They substitute the person, animal or object performing the action of the sentence.
The eight subject personal pronouns are:
| Pronoun | Person and gender | Refers to | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | first person singular, masculine and feminine | yourself | I love dogs. |
| you | second person singular, masculine and feminine | a single other person | You aren't tired, are you? |
| he | third person singular, masculine | one single male | He is a doctor. |
| she | third person singular, feminine | one single female | She loves running. |
| it | third person singular, neuter | one single thing | It was left on the street. |
| we | first person plural, masculine and feminine | a group that includes yourself | We are going to the cinema. |
| you, you all | second person plural, masculine and feminine | a group outside yourself | You all are hungry, right? |
| they | third person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include present company | They made a reservation at the burger restaurant. |
Object Personal Pronouns
Object personal pronouns function as objects of sentences.
Here’s the full list of object personal pronouns:
| Pronoun | Person and gender | Refers to | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| me | first person singular, masculine or feminine | yourself | It sounds good to me. |
| you | second person singular, masculine or feminine | someone else | I like you. |
| him | third person singular, masculine | one other male | The car belongs to him. |
| her | third person singular, feminine | one other female | I like her a lot. |
| it | third person singular, neuter | one thing | I lost it at the beach. |
| us | first person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that includes yourself | It's too expensive for us. |
| you, you all | second person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include yourself | I'm coming to dinner with you all. |
| them | third person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include yourself and aren't present | The crime was committed by them. |
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are the pronouns that help us talk about possession and ownership (who owns what).
Possessive pronouns also have different forms depending on the grammatical person. They can also change depending on the gender of the noun (in the third person singular), but they do not show number in English:
This is my book. → It is mine.
These are my books. → They are mine.
As with the personal pronouns, we have one possessive pronoun for each grammatical person:
| Pronoun | Person and gender | Refers to | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| mine | first person singular or plural, masculine or feminine | yourself | The dog is mine. |
| yours | second person singular or plural, masculine or feminine | someone else | Is this ring yours? |
| his | third person singular or plural, masculine | a single male | That's his car. |
| hers | third person singular or plural, feminine | a single female | Those cats are hers. |
| its | third person singular or plural, neuter | a single thing | Its tires are flat. |
| ours | first person singular or plural, masculine or feminine | a group that includes yourself | The dinner reservations are ours. |
| yours | second person singular or plural, masculine or feminine | a present group that doesn't include yourself | Is this key yours? [to a couple] |
| theirs | third person singular or plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include yourself and isn't present | I don't know where this lemonade came from, I think it's theirs. |
3. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are the pronouns we use to refer and point to specific people, animals and things.
The four main demonstrative pronouns are:
| Pronoun | Distance | Number | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| this | close | singular | This is so exciting. |
| that | far | singular | That was delicious. |
| these | close | plural | These fit really well. |
| those | far | plural | Those aren't the right color. |
As you can see, the only two things we have to take into account when using them is the distance (in space or time) from the speaker and the number of the noun they are referring to.
4. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns are pronouns that refer mainly to non-specific people, animals, things and quantities.
This means they do not refer to specific nouns. Instead, they refer to any noun of the category the speaker is talking about:
Anybody can do it. (Any person can do it.)
I already have enough to build a castle. (I have a non-specific amount of something, perhaps sand, to build a castle.)
The group of indefinite pronouns is the biggest one. The main pronouns included in this group are:
another, other, anybody, anyone, somebody, someone, nobody, no one, everybody, everyone, nothing, anything, something, everything, each, either, neither, one, enough, less, little, much, more, both, few, fewer, several, many, others, all, any, most, least, some, such, none
As you can see, they are super varied and could be grouped into several subcategories, for example, pronouns that:
- only refer to people: anybody, anyone, somebody, someone, nobody, no one, everybody, everyone.
- only refer to things: anything, something, nothing, everything.
- only refer to countable nouns: few, fewer, several, many, others.
- only refer to uncountable nouns: little, less, least.
5. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are a small group of pronouns that introduce relative clauses.
They are called “relative” because they refer to the noun described or modified by the relative clause. A basic way to tell if a part of a sentence is a relative clause is to remove it—if the sentence still makes sense without it, then it is a relative clause!
The English relative pronouns are:
| Pronoun | Refers to | Example |
|---|---|---|
| who/whom | people | The runner who won the race was 35. |
| which | animals and things | Pasta, which we eat once a week, is my favorite food. |
| that | people, animals and things | The dress I bought last week is green. |
| whose | people, animals and things | The boy whose hair is red is winning the race. |
6. Interrogative Pronouns
The set of interrogative pronouns looks almost identical to the relative pronouns (except for that becoming what).
This group of pronouns does not describe or give information about a noun.
Instead, interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions about people, animals, things and possessors:
| Pronoun | To ask about | Example |
|---|---|---|
| who/whom | people | Who is that woman? |
| which | animals and things | Which shirt do you like best? |
| what | people, animals and things | What is he doing over there? |
| whose | people, animals and things (possessive) | Whose cat is this? |
7. Reflexive Pronouns
The reflexive pronouns are used when a person, animal or object performs (does) an action on themselves, such as bathing or washing (oneself).
This is another group of pronouns that has a different form for each grammatical person:
| Pronoun | Person and gender | Refers to | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| myself | first person singular, masculine or feminine | yourself | If I want the job done well, I have to do it myself. |
| yourself | second person singular, masculine or feminine | another single person | Do it yourself! |
| himself | third person singular, masculine | a single male | He made the lasagna all by himself. |
| herself | third person singular, feminine | a single female | She got the job done by herself. |
| itself | third person singular, neuter | a single thing | That fire started by itself. |
| ourselves | first person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that includes yourself | We're going to have to do this ourselves I'm afraid. |
| yourselves | second person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include yourself | I don't want to clean the house. Do it yourselves. |
| themselves | third person plural, masculine or feminine | a group that doesn't include yourself and isn't present | They built the house themselves. |
Notice how the second person singular and the second person plural are different, which happens very rarely in English.
You might be asking why we need a set of reflexive pronouns to refer to a subject when we can just use the same subject once again. Well, reflexive pronouns help us avoid misunderstandings and sentences that would sound very weird or just be ungrammatical.
8. Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are a very special type of English pronoun.
There are only two of them:
| Pronoun | Number | Example |
|---|---|---|
| each other | two people | They love each other deeply. |
| one another | more than two people | They all shook hands with one another. |
They are used when two or more people perform a reciprocal action: an action that everyone in the situation is either doing or having it done to them.
Try not to confuse reflexive and reciprocal pronouns. Sometimes they make sentences look very similar in meaning to learners, but they only seem similar. The reality is different:
We love ourselves. (I love myself and my friend loves himself, but we do not love each other.)
We love each other. (I love her and she loves me, but I do not necessarily love myself or she herself.)
9. Intensive Pronouns
The intensive pronouns are used to add emphasis or importance to the subject or antecedent of a sentence.
They look identical to the reflexive pronouns, but they are used differently.
While reflexive pronouns refer to a subject performing an action on itself, intensive pronouns refer to a subject that is not doing anything to itself. We just want to emphasize the subject of the sentence:
I did it myself. (I did it on my own, no one helped me.)
She wrote the article herself. Can you believe it? (She wrote the article without any help.)
A quick trick to decide if a pronoun is reflexive or intensive is to try to remove it from the sentence. If this is possible, the pronoun is intensive. If it is not possible, the pronoun is reflexive:
I cut the paper myself. (I cut the paper makes sense, so this is an intensive pronoun.)
I cut myself last week. (I cut last week does not make sense, so this is a reflexive pronoun.)
As you can see, English pronouns are as varied as they are necessary.
We may not be aware of this, but we constantly use pronouns when we speak or write in English, so the sooner you learn them, the better. You can see for yourself by picking a random video on YouTube or FluentU to watch, then counting how many pronouns appear on it. If you use FluentU, you can also save the pronouns to a flashcard deck and view other videos where they appear for additional context.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Each set of pronouns has its own characteristics, but remember that all pronouns share two traits: They substitute a noun and they work on their own.
Now that you have finished reading the post, pick a couple of pronouns from each group and try to write some sample sentences with them. Remember that practice makes perfect, and this is especially true when we are dealing with grammar topics.
Let’s see each other in the next post. Or one another, if you bring a friend with you.
Stay curious, my friends and, as always, happy learning!
And One More Thing...
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
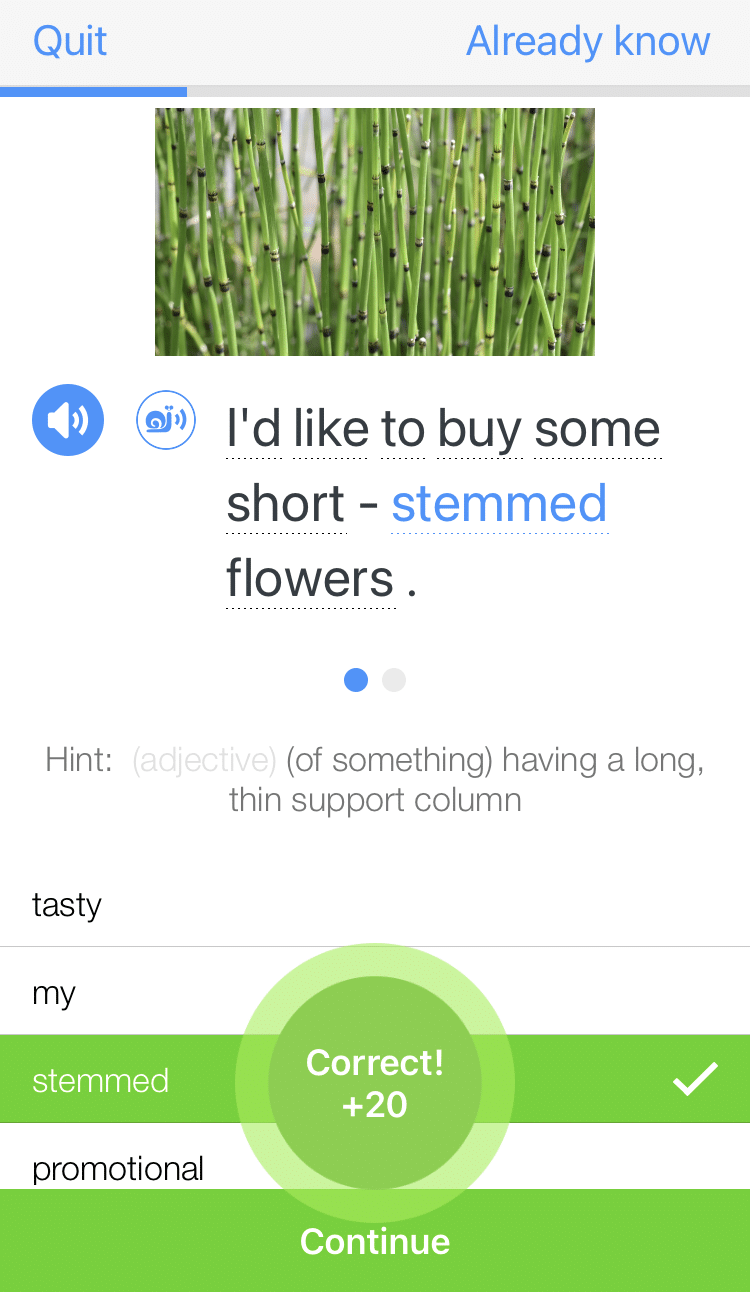
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)