English Future Continuous Tense
You may already be familiar with the future simple tense, as in “I will study English tomorrow.”
But what about the future continuous tense?
Normally, the future continuous is used to discuss plans that will take place some time in the future.
If that’s still a little too vague (unclear) for you, let’s get right into discussing this important tense!
Contents
- What Is the English Future Continuous Tense?
- English Future Continuous vs. Future Simple: What’s the Difference?
- How to Form the English Future Continuous Tense
- How to Use the English Future Continuous Tense
- How to Make the English Future Continuous Negative
- How to Form Questions in the Future Continuous Tense
- And One More Thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What Is the English Future Continuous Tense?
The future continuous tense, also known as the future progressive tense, is an English tense that’s used to talk about continuous actions that will occur in the future. It’s typically formed as follows: will + be + “-ing” form of the verb.
For example, if somebody asked you what you’ll be doing tomorrow afternoon, you could reply:
I will be studying English future tenses!
I’ll be studying English future tenses!
Both are essentially the same sentence, except the second one uses the “I’ll” (I + will) contraction.
Notice how the sentence refers to both the future and ongoing action. Also, notice how there’s an assumption that the action will be completed, even though we never said it will be.
English Future Continuous vs. Future Simple: What’s the Difference?
To understand the difference between the English future simple and future continuous, we’re going to look at a couple of sentences.
First, let’s take a look at an example in the future simple tense:
Here, we expect something to happen in the near future. Notice that there’s also an implied ending to the tense. We also know when the action will begin—at five o’clock!
Now, let’s use the future continuous version of the same sentence:
I will be eating at 5 pm.
I’ll be eating at 5 pm.
This time, we don’t know when the action will begin. We only know that it will begin in the future and that it will still be happening at five o’clock.
Put simply, the English future tense typically expresses the speaker’s personal predictions, while the English future continuous tense typically has a stronger grounding in fact.
As you can see, the correct use of future tenses in English generally depends on the circumstances of the individual talking just as much as the language itself. In order to figure out the best use of these tenses, you need to familiarize yourself with English future tenses in a native context.
For example, you can get a language exchange partner to practice your general conversational skills. You can also experience English tenses through English media by watching TV shows and movies, listening to music and watching videos on a language learning platform like FluentU.
How to Form the English Future Continuous Tense
To form the English future continuous tense, follow this simple pattern:
(Subject) + will + be + (-ing form of the root verb)
For example:
The good news about this formula is that you don’t need to conjugate the to be verb. Also, in this case, will is used as an auxiliary verb.
Sometimes, you’ll also see the word “shall” used in place of “will,” as in “I shall be eating.” However, this sounds like an older form of English and sounds a bit old-fashioned (not modern). It could even sound a bit strange.
You could also use “going to” , as in “I’m going to be eating.” However, like “shall,” “going to” isn’t as common as “will.”
Therefore, from here on out, we’re going to form the English future continuous using “will.”
How to Use the English Future Continuous Tense
Describe Interrupted Actions in the Future
One of the most common uses of the future continuous tense is to describe a situation where a longer action (ongoing) will be interrupted by another shorter action (in the future).
For example:
I will be cooking when the TV show starts.
I’ll be cooking when the TV show starts.
I will be sleeping when your plane lands at the airport.
I’ll be sleeping when your plane lands at the airport.
Notice what these sentences have in common?
As you can see, when using the future continuous to describe interrupted actions, the word when is commonly used.
Talk About Two Future Actions Happening at the Same Time
When two actions are happening at the same time, they can also be referred to as “parallel actions”—and the future continuous tense often makes use of this as well.
For example:
I will be fishing while you look for a place to stay.
I’ll be fishing while you look for a place to stay.
He will be swimming while she is sailing.
He’ll be swimming while she’s sailing.
When the future continuous tense is used this way, the sentences often use the word while.
Reassure Someone
If you’re looking to reassure (comfort) somebody regarding a future action that you’ll be taking, you’ll probably be using the future continuous as well.
For example, let’s say you offered to give somebody a lift (a ride) in your car. If you’d like to reassure them that you’re able to give them a ride, you can say something like:
How to Make the English Future Continuous Negative
Forming the negative in the future continuous is very simple.
All you have to do is add not before the verb “to be” and the -ing verb. If you’re using contractions, remember that the contracted form of “will not” is won’t.
He will not be coming home too late.
He won’t be coming home too late.
They will not be studying any Shakespeare this week.
They won’t be studying any Shakespeare this week.
How to Form Questions in the Future Continuous Tense
Using the future continuous tense is an excellent way to ask a polite question or even request a favor.
Remember our formula? See if you can notice a slight change below:
Will + subject + verb + to be + -ing verb
Let’s look at some example sentences:
Will you be playing football tonight?
Will we be staying in a hotel or a hostel this weekend?
As you can see, if you’re asking a “yes or no” question, simply swap the subject for the auxiliary verb.
If you’re asking a wh- question, just tack on the wh- word at the beginning of the sentence.
For example:
Where will you be playing football tonight?
I hope you enjoyed this post on the English future continuous tense. While the future continuous may sometimes be overlooked, it’s a very important grammatical point for talking about the future with accuracy and confidence.
Best of luck!
And One More Thing...
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
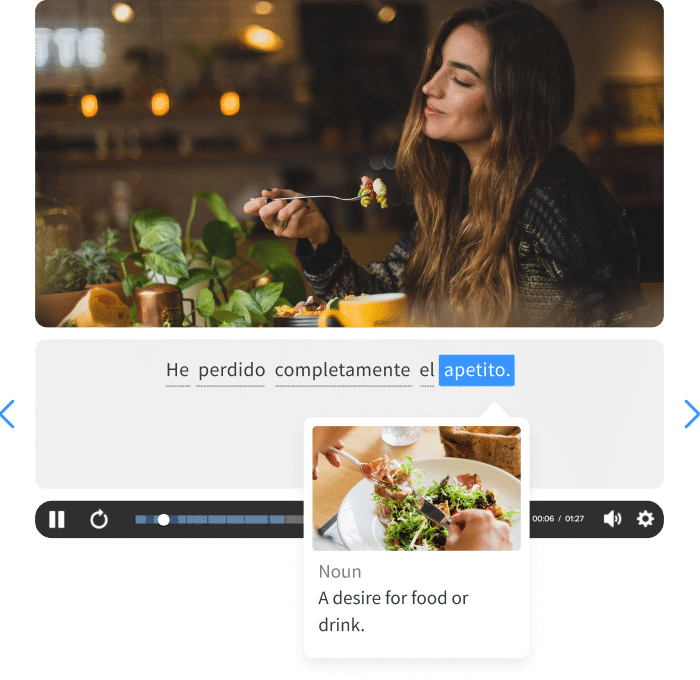
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
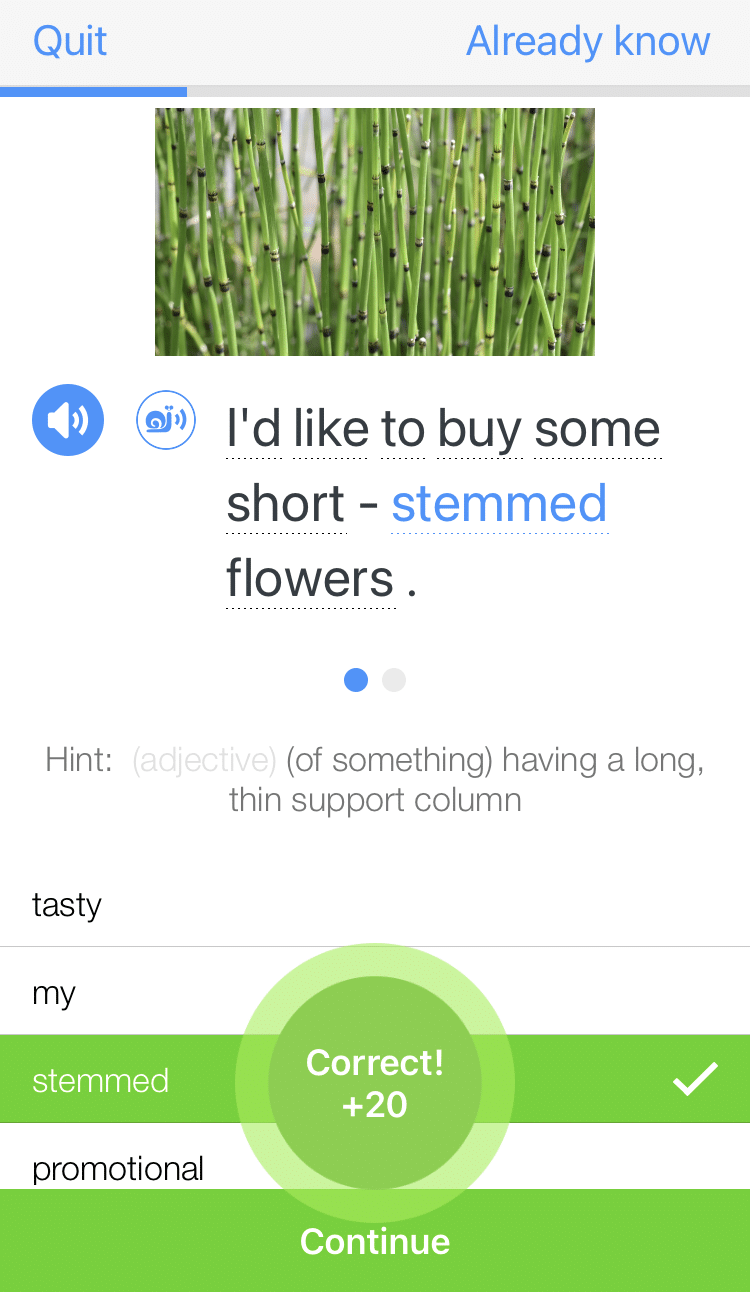
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)